CNN Example
Convolutional neural network (CNN) is a type of feed-forward artificial neural network widely used for image and video classification. In this example, we will use a deep CNN model to do image classification for the CIFAR10 dataset.
Running instructions
Please refer to the installation page for instructions on building SINGA, and the quick start for instructions on starting zookeeper.
We have provided scripts for preparing the training and test dataset in examples/cifar10/.
# in examples/cifar10 $ cp Makefile.example Makefile $ make download $ make create
We can start the training by
./bin/singa-run.sh -conf examples/cifar10/job.conf
You should see output like
Record job information to /tmp/singa-log/job-info/job-2-20150817-055601 Executing : ./singa -conf /xxx/incubator-singa/examples/cifar10/job.conf -singa_conf /xxx/incubator-singa/conf/singa.conf -singa_job 2 E0817 06:56:18.868259 33849 cluster.cc:51] proc #0 -> 192.168.5.128:49152 (pid = 33849) E0817 06:56:18.928452 33871 server.cc:36] Server (group = 0, id = 0) start E0817 06:56:18.928469 33872 worker.cc:134] Worker (group = 0, id = 0) start E0817 06:57:13.657302 33849 trainer.cc:373] Test step-0, loss : 2.302588, accuracy : 0.077900 E0817 06:57:17.626708 33849 trainer.cc:373] Train step-0, loss : 2.302578, accuracy : 0.062500 E0817 06:57:24.142645 33849 trainer.cc:373] Train step-30, loss : 2.302404, accuracy : 0.131250 E0817 06:57:30.813354 33849 trainer.cc:373] Train step-60, loss : 2.302248, accuracy : 0.156250 E0817 06:57:37.556655 33849 trainer.cc:373] Train step-90, loss : 2.301849, accuracy : 0.175000 E0817 06:57:44.971276 33849 trainer.cc:373] Train step-120, loss : 2.301077, accuracy : 0.137500 E0817 06:57:51.801949 33849 trainer.cc:373] Train step-150, loss : 2.300410, accuracy : 0.135417 E0817 06:57:58.682281 33849 trainer.cc:373] Train step-180, loss : 2.300067, accuracy : 0.127083 E0817 06:58:05.578366 33849 trainer.cc:373] Train step-210, loss : 2.300143, accuracy : 0.154167 E0817 06:58:12.518497 33849 trainer.cc:373] Train step-240, loss : 2.295912, accuracy : 0.185417
After training some steps (depends on the setting) or the job is finished, SINGA will checkpoint the model parameters.
Details
To train a model in SINGA, you need to prepare the datasets, and a job configuration which specifies the neural net structure, training algorithm (BP or CD), SGD update algorithm (e.g. Adagrad), number of training/test steps, etc.
Data preparation
Before using SINGA, you need to write a program to convert the dataset into a format that SINGA can read. Please refer to the Data Preparation to get details about preparing this CIFAR10 dataset.
Neural net
Figure 1 shows the net structure of the CNN model we used in this example, which is set following Alex The dashed circle represents one feature transformation stage, which generally has four layers as shown in the figure. Sometimes the rectifier layer and normalization layer are omitted or swapped in one stage. For this example, there are 3 such stages.
Next we follow the guide in neural net page and layer page to write the neural net configuration.
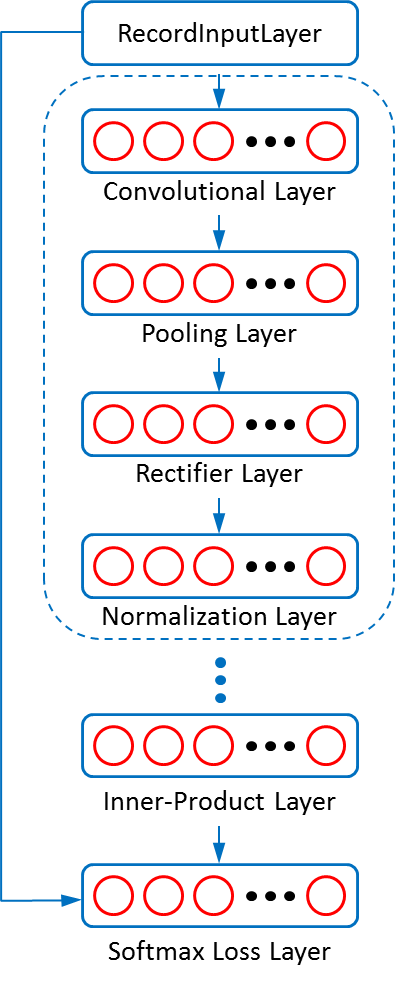
Figure 1 - Net structure of the CNN example.
-
We configure a data layer to read the training/testing Records from DataShard.
layer{ name: "data" type: kShardData sharddata_conf { path: "examples/cifar10/cifar10_train_shard" batchsize: 16 random_skip: 5000 } exclude: kTest # exclude this layer for the testing net } layer{ name: "data" type: kShardData sharddata_conf { path: "examples/cifar10/cifar10_test_shard" batchsize: 100 } exclude: kTrain # exclude this layer for the training net } -
We configure two parser layers to extract the image feature and label from Recordss loaded by the data layer.
layer{ name:"rgb" type: kRGBImage srclayers: "data" rgbimage_conf {...} } layer{ name: "label" type: kLabel srclayers: "data" } -
We configure layers for the feature transformation as follows (all layers are built-in layers in SINGA; hyper-parameters of these layers are set according to Alex’s setting).
layer { name: "conv1" type: kConvolution srclayers: "rgb" convolution_conf {... } ... } layer { name: "pool1" type: kPooling srclayers: "conv1" pooling_conf {... } } layer { name: "relu1" type: kReLU srclayers:"pool1" } layer { name: "norm1" type: kLRN lrn_conf {... } srclayers:"relu1" }
The configurations for another 2 stages are omitted here.
-
There is an inner product layer after the 3 transformation stages, which is configured with 10 output units, i.e., the number of total labels. The weight matrix Param is configured with a large weight decay scale to reduce the over-fitting.
layer { name: "ip1" type: kInnerProduct srclayers:"pool3" innerproduct_conf { num_output: 10 } param { name: "w4" wd_scale:250 ... } param { name: "b4" ... } } -
The last layer is a Softmax loss layer
layer{ name: "loss" type: kSoftmaxLoss softmaxloss_conf{ topk:1 } srclayers:"ip1" srclayers: "label" }
Updater
The normal SGD updater is selected. The learning rate is changed like going down stairs, and is configured using the kFixedStep type.
updater{
type: kSGD
weight_decay:0.004
learning_rate {
type: kFixedStep
fixedstep_conf:{
step:0 # lr for step 0-60000 is 0.001
step:60000 # lr for step 60000-65000 is 0.0001
step:65000 # lr for step 650000- is 0.00001
step_lr:0.001
step_lr:0.0001
step_lr:0.00001
}
}
}
TrainOneBatch algorithm
The CNN model is a feed forward model, thus should be configured to use the Back-propagation algorithm.
train_one_batch {
alg: kBP
}
Cluster setting
The following configuration set a single worker and server for training. Training frameworks page introduces configurations of a couple of distributed training frameworks.
cluster {
nworker_groups: 1
nserver_groups: 1
}



