Since we're on a major migration process of this website, some component documents here are out of sync right now. In the meantime you may want to look at the early version of the new website
https://camel.apache.org/staging/
We would very much like to receive any feedback on the new site, please join the discussion on the Camel user mailing list.
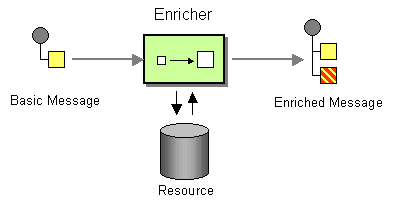
Content EnricherCamel supports the Content Enricher from the EIP patterns using a Message Translator, an arbitrary Processor in the routing logic, or using the enrich DSL element to enrich the message. Content enrichment using a Message Translator or a ProcessorUsing the Fluent Builders You can use Templating to consume a message from one destination, transform it with something like Velocity or XQuery, and then send it on to another destination. For example using InOnly (one way messaging) If you want to use InOut (request-reply) semantics to process requests on the My.Queue queue on ActiveMQ with a template generated response, then sending responses back to the JMSReplyTo Destination you could use this: Here is a simple example using the DSL directly to transform the message body For further examples of this pattern in use you could look at one of the JUnit tests Using Spring XML Content enrichment using the |
Name | Default Value | Description |
|---|---|---|
|
| The endpoint uri for the external service to enrich from. You must use either |
|
| Refers to the endpoint for the external service to enrich from. You must use either |
| expression | Camel 2.16: Mandatory. The Expression to configure the uri, such as Simple or Constant or any other dynamic language that can compute the uri dynamically using values from the current Exchange. | |
|
| Refers to an AggregationStrategy to be used to merge the reply from the external service, into a single outgoing message. By default Camel will use the reply from the external service as outgoing message. From Camel 2.12 onwards you can also use a POJO as the |
|
| Camel 2.12: This option can be used to explicit declare the method name to use, when using POJOs as the |
|
| Camel 2.12: If this option is |
aggregateOnException | false | Camel 2.14: If this option is false then the aggregate method is not used if there was an exception thrown while trying to retrieve the data to enrich from the resource. Setting this option to true allows end users to control what to do if there was an exception in the aggregate method. For example to suppress the exception or set a custom message body etc. |
shareUnitOfWork | false | Camel 2.16: Shares the unit of work with the parent and the resource exchange. Enrich will by default not share unit of work between the parent exchange and the resource exchange. This means the resource exchange has its own individual unit of work. See Splitter for more information and example. |
cacheSize | Camel 2.16: Allows to configure the cache size for the ProducerCache which caches producers for reuse in the enrich. Will by default use the default cache size which is 1000. Setting the value to -1 allows to turn off the cache all together. | |
ignoreInvalidEndpoint | false | Camel 2.16: Whether to ignore an endpoint URI that could not be resolved. If disabled, Camel will throw an exception identifying the invalid endpoint URI. |
Using the Fluent Builders
The content enricher (enrich) retrieves additional data from a resource endpoint in order to enrich an incoming message (contained in the original exchange). An aggregation strategy is used to combine the original exchange and the resource exchange. The first parameter of the AggregationStrategy.aggregate(Exchange, Exchange) method corresponds to the the original exchange, the second parameter the resource exchange. The results from the resource endpoint are stored in the resource exchange's out-message. Here's an example template for implementing an aggregation strategy:
Using this template the original exchange can be of any pattern. The resource exchange created by the enricher is always an in-out exchange.
Using Spring XML
The same example in the Spring DSL (Camel 2.15 or older)
The same example in the Spring DSL (Camel 2.16 or newer)
Aggregation strategy is optional
The aggregation strategy is optional. If you do not provide it Camel will by default just use the body obtained from the resource.
In the route above the message sent to the direct:result endpoint will contain the output from the direct:resource as we do not use any custom aggregation.
And for Spring DSL (Camel 2.15 or older) just omit the strategyRef attribute:
And for Spring DSL (Camel 2.16 or newer) just omit the strategyRef attribute:
Using dynamic uris
Available as of Camel 2.16
From Camel 2.16 onwards enrich and pollEnrich supports using dynamic uris computed based on information from the current Exchange. For example to enrich from a HTTP endpoint where the header with key orderId is used as part of the content-path of the HTTP url:
And in XML DSL
Content enrichment using pollEnrich
The pollEnrich works just as the enrich however as it uses a Polling Consumer we have 3 methods when polling
- receive
- receiveNoWait
- receive(timeout)
PollEnrich Options
Name | Default Value | Description |
|---|---|---|
|
| The endpoint uri for the external service to enrich from. You must use either |
|
| Refers to the endpoint for the external service to enrich from. You must use either |
expression | Camel 2.16: Mandatory. The Expression to configure the uri, such as Simple or Constant or any other dynamic language that can compute the uri dynamically using values from the current Exchange. | |
|
| Refers to an AggregationStrategy to be used to merge the reply from the external service, into a single outgoing message. By default Camel will use the reply from the external service as outgoing message. From Camel 2.12 onwards you can also use a POJO as the |
|
| Camel 2.12: This option can be used to explicit declare the method name to use, when using POJOs as the |
|
| Camel 2.12: If this option is |
|
| Timeout in millis when polling from the external service. See below for important details about the timeout. |
aggregateOnException | false | Camel 2.14: If this option is false then the aggregate method is not used if there was an exception thrown while trying to retrieve the data to enrich from the resource. Setting this option to true allows end users to control what to do if there was an exception in the aggregate method. For example to suppress the exception or set a custom message body etc. |
cacheSize | Camel 2.16: Allows to configure the cache size for the ConsumerCache which caches consumers for reuse in the pollEnrich. Will by default use the default cache size which is 1000. Setting the value to -1 allows to turn off the cache all together. | |
ignoreInvalidEndpoint | false | Camel 2.16: Whether to ignore an endpoint URI that could not be resolved. If disabled, Camel will throw an exception identifying the invalid endpoint URI. |
By default Camel will use the receive. Which may block until there is a message available. It is therefore recommended to always provide a timeout value, to make this clear that we may wait for a message, until the timeout is hit.
If there is no data then the newExchange in the aggregation strategy is null.
You can pass in a timeout value that determines which method to use
- if timeout is -1 or other negative number then
receiveis selected (Important: thereceivemethod may block if there is no message) - if timeout is 0 then
receiveNoWaitis selected - otherwise
receive(timeout)is selected
The timeout values is in millis.
pollEnrich does not access any data from the current Exchange which means when polling it cannot use any of the existing headers you may have set on the Exchange. For example you cannot set a filename in the Exchange.FILE_NAME header and use pollEnrich to consume only that file. For that you must set the filename in the endpoint URI.
From Camel 2.16 onwards both enrich and pollEnrich supports dynamic endpoints that uses an Expression to compute the uri, which allows to use data from the current Exchange. In other words all what is told above no longer apply and it just works.
Example
In this example we enrich the message by loading the content from the file named inbox/data.txt.
And in XML DSL (Camel 2.15 or older) you do:
And in XML DSL (Camel 2.16 or newer) you do:
If there is no file then the message is empty. We can use a timeout to either wait (potentially forever) until a file exists, or use a timeout to wait a certain period.
For example to wait up to 5 seconds you can do (Camel 2.15 or older):
For example to wait up to 5 seconds you can do (Camel 2.16 or newer):
Using dynamic uris
Available as of Camel 2.16
From Camel 2.16 onwards enrich and pollEnrich supports using dynamic uris computed based on information from the current Exchange. For example to pollEnrich from an endpoint that uses a header to indicate a SEDA queue name:
And in XML DSL