Programming Guide
To submit a training job, users must provide the configuration of the four components shown in Figure 1:
- a NeuralNet describing the neural net structure with the detailed layer setting and their connections;
- a TrainOneBatch algorithm which is tailored for different model categories;
- an Updater defining the protocol for updating parameters at the server side;
- a Cluster Topology specifying the distributed architecture of workers and servers.
The Basic user guide section describes how to submit a training job using built-in components; while the Advanced user guide section presents details on writing user’s own main function to register components implemented by themselves. In addition, the training data must be prepared, which has the same process for both advanced users and basic users.
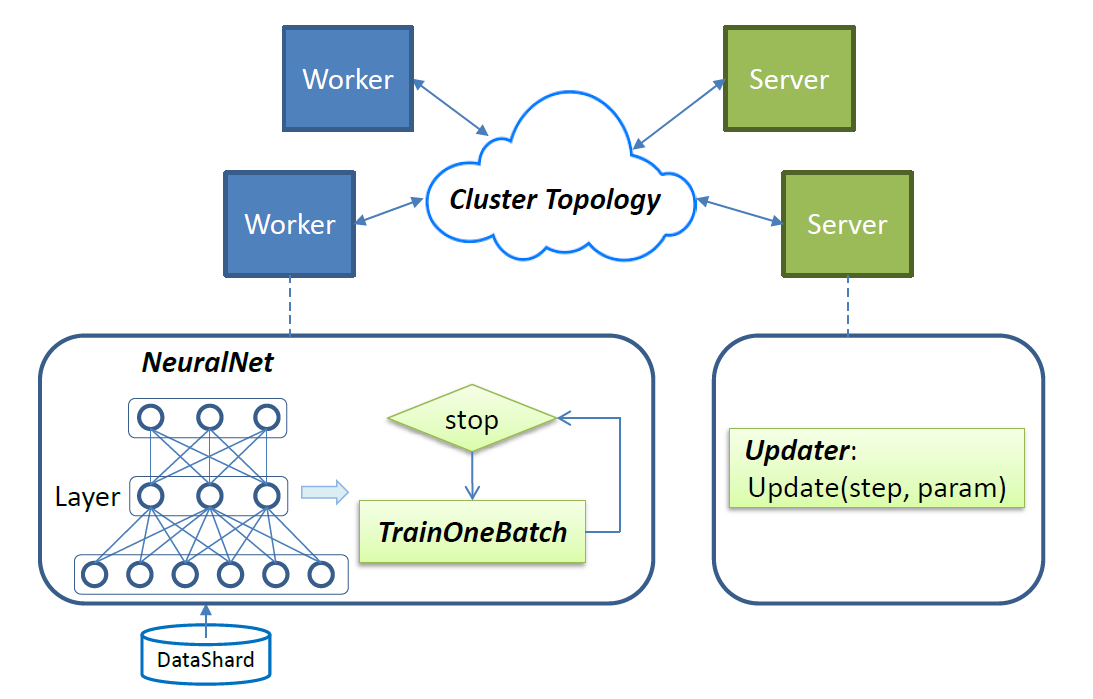 Figure 1 - SINGA overview.
Figure 1 - SINGA overview.
Basic user guide
Users can use the default main function provided SINGA to submit the training job. For this case, a job configuration file written as a google protocol buffer message for the JobProto must be provided in the command line,
./bin/singa-run.sh -conf <path to job conf> [-resume]
-resume is for continuing the training from last checkpoint. The MLP and CNN examples use built-in components. Please read the corresponding pages for their job configuration files. The subsequent pages will illustrate the details on each component of the configuration.
Advanced user guide
If a user’s model contains some user-defined components, e.g., Updater, he has to write a main function to register these components. It is similar to Hadoop’s main function. Generally, the main function should
-
initialize SINGA, e.g., setup logging.
-
register user-defined components.
-
create and pass the job configuration to SINGA driver
An example main function is like
#include "singa.h"
#include "user.h" // header for user code
int main(int argc, char** argv) {
singa::Driver driver;
driver.Init(argc, argv);
bool resume;
// parse resume option from argv.
// register user defined layers
driver.RegisterLayer<FooLayer>(kFooLayer);
// register user defined updater
driver.RegisterUpdater<FooUpdater>(kFooUpdater);
...
auto jobConf = driver.job_conf();
// update jobConf
driver.Train(resume, jobConf);
return 0;
}
The Driver class’ Init method will load a job configuration file provided by users as a command line argument (-conf <job conf>). It contains at least the cluster topology and returns the jobConf for users to update or fill in configurations of neural net, updater, etc. If users define subclasses of Layer, Updater, Worker and Param, they should register them through the driver. Finally, the job configuration is submitted to the driver which starts the training.
We will provide helper functions to make the configuration easier in the future, like keras.
Users need to compile and link their code (e.g., layer implementations and the main file) with SINGA library (.libs/libsinga.so) to generate an executable file, e.g., with name mysinga. To launch the program, users just pass the path of the mysinga and base job configuration to ./bin/singa-run.sh.
./bin/singa-run.sh -conf <path to job conf> -exec <path to mysinga> [other arguments]
The RNN application provides a full example of implementing the main function for training a specific RNN model.



