Manipulating Content - The SlingPostServlet (servlets.post)
- Multiple Ways to Modify Content
- Quickstart: Creating Content
- Preface: multipart/form-data POSTs
- SlingPostServlet Operations
- Content Creation or Modification
- Content Removal
- Copying Content
- Moving Content
- Importing Content Structures
- Null Operation
- Special Parameters
- Response format
- Versionable Node Support
- Extending the SlingPostServlet
Multiple Ways to Modify Content¶
As always in life there is more than one way to do it. So to modify content in a JCR repository underlying Sling, you have multiple options, two of which are WebDAV and the Sling default POST Servlet also called the SlingPostServlet. This page is about how you can modify - create, modify, copy, move, delete, import - content through the SlingPostServlet. In addition it also explains how to extend the SlingPostServlet with new operations.
What is Content anyway? In the following discussion, I use the terms Content and Item interchangeably. With Content I just mean some data to be stored in the JCR repository to be later used as the basis for some presentation. In this sense Content is a rather conceptual term. Item is the name of the parent interface of the JCR Node and Property interfaces. When speaking of Items we mean some actual data stored in the repository ignoring whether the data is actually stored as a Node with child nodes and properties or just a single Property.
Quickstart: Creating Content¶
To create content you simply send an HTTP POST request using the path of the node to store the content in and include the actual content as request parameters. So one possibility to do just that is by having an HTML Form like the following:
<form method="POST" action="http://host/some/new/content" enctype="multipart/form-data"> <input type="text" name="title" value="" /> <input type="text" name="text" value="" /> </form>
This simple form will set the title and text properties on a node at /some/new/content. If this node does not exist it is just created otherwise the existing content would be modified.
Similarly, you can do this using the curl command line tool:
$ curl -Ftitle="some title text" -Ftext="some body text content" http://host/some/new/content
You might want to use a specific JCR node type for a newly created node. This is possible by simply setting a jcr:primaryType property on the request, e.g.
$ curl -F"jcr:primaryType=nt:unstructured" -Ftitle="some title text" \ -Ftext="some body text content" http://host/some/new/content
Similarly, you may assign JCR mixin node types using the jcr:mixinTypes property and a Sling resource type using the sling:resourceType property. For example:
$ curl -F"sling:resourceType=sling:sample" -Ftitle="some title text" \ -Ftext="some body text content" http://host/some/new/content
Preface: multipart/form-data POSTs¶
Sometimes you might want to have the content modifications applied in a certain order. This is particularly interesting if you use fields to create child nodes and if you want to stipulate a certain child node order based on the form fields.
In this case, ensure you are submitting the POST request using multipart/form-data encoding. This preserves the order of parameter application according to the original HTML form. To this avail, ensure to always include the enctype="multipart/form-data" attribute with the <form> tag.
This support requires Sling Engine 2.1.0 and the Sling Default Post Servlet 2.0.6.
SlingPostServlet Operations¶
The SlingPostServlet is actually just a front-end to the actual operations. To select the actual operation to execute, the :operation request parameter is used. Out of the box, the SlingPostServlet supports the following operations:
- property not set or empty -- Create new content or modify existing content
delete-- Remove existing contentmove-- Move existing content to a new locationcopy-- Copy existing content to a new locationimport-- Import content structures from JSON/XML/Zipnop-- Explicitly requests to do nothing and just sets the response statuscheckin- Check in a versionable nodecheckout- Check out a versionable node
All these operations always operate on the resource of the request as returned by SlingHttpServletRequest.getResource(). Some operations require additional parameters to be set to operate completely.
Please note that operations are mutually exclusive. For a single POST request only one operation may be executed. Operations also only consume the request parameters as described below. Any excess parameters are silently ignored.
Content Creation or Modification¶
The simplest and most common use case, probably, is content creation and modification. We already saw an example above in the quickstart section. In this section we elaborate more on the concrete stuff.
First, the request URL indicates the actual repository node to be handled. If the URL addresses an existing node, the request parameters just provide values for the properties to be set on the existing node.
If the resource of the request is a synthetic resource, e.g. NonExistingResource or StarResource, a new item is created. The path (including name) of the item to be created is derived from the resource path:
- If the resource path ends with a
/*or/the name of the item is automatically created using a name creation algorithm taking into account various request parameters. - Otherwise the resource path is used as the path and name of the new item.
In both cases the path may still include selectors and extensions, which are cut off the path before finding out, what to do.
To illustrate this algorithm, lets look at some examples (and check the PostServletCreateTest in case of doubt):
| Resource Path | Item path |
|---|---|
/content/new |
/content/new |
/content/new.html |
/content/new |
/content/new.print.a4.html |
/content/new |
/content/ |
/content/xxx where xxx is a generated name |
/content/* |
/content/xxx where xxx is a generated name |
/content/*.html |
/content/xxx where xxx is a generated name |
/content/*.print.a4.html |
/content/xxx where xxx is a generated name |
Setting Property Values¶
Setting property values is as simple as just adding a request parameter whose name is the name of the property to be set and whose value is the value to be assigned to the property. We already saw how to do this in the quick start examples above.
Here is another example show a simple HTML form to create a new node with an automatically created name:
<form method="POST" action="/content/page/first" enctype="multipart/form-data"> <input type="text" name="title" /> <input type="text" name="text" /> <input type="Submit" /> </form>
If this form is submitted with title and This is some Text as values for the title and text fields respectively, a new node is created at the path /content/page/first and the title and text properties set to the respective field values. If a node at /content/page/first already existed before submitting the form, the title and text properties are just updated to the new values from the form fields.
If a parameter has multiple values, the respective property will be created as a multi-value property. So for example the command line:
$ curl -Fmulti=one -Fmulti=two http://host/content/page
Would assign the /content/page/multi property the value [ "one", "two" ].
This is pretty much all there is to know about creating and modifying content. The following sections will now introduce more functionality which help you with more fine-grained control in your content management application.
Automatic property values: last modified and created by¶
To make it easier to set "last modified" and "created by" property values from POST requests, values are generated automatically for the following property names if they are supplied with empty values in such a request:
-
createdandjcr:createdare set to the node creation time, as a Date value. -
lastModified,jcr:lastModifiedare set to the node modification time, as a Date value. -
createdByandjcr:createdByare set to the name of the user who created the node. -
lastModifiedBy,jcr:lastModifiedByare set to the name of the user who modified the node.
This is demonstrated by the SlingAutoPropertiesTest which is part of our launchpad integration tests.
File Uploads¶
File uploads are typically done using the <input type="file""/> element of an HTML form and ensuring the correct form encoding. The SlingPostServlet handles uploaded files specially, in that the file data is not simply written into a property, but a node is actually created with three properties:
jcr:data-- The actual file contentsjcr:lastModified-- The time stamp of processing the uploaded filejcr:mimeType-- The MIME type from the original file submission (if contained in the file body part) or derived from the original file name
The name of the node is either taken from the parameter name or if the name is * from the name of the uploaded file.
The primary node type of the uploaded file is selected using the following algorithm:
- If a `@TypeHint suffixed parameter (see below for a description) is present check whether the value is a known non-mixin node type. If so, the node is created with this primary node type.
- If a
@TypeHintsuffixed parameter is not present or the value does not denote an existing non-mixin node type, the node will be created as annt:filenode if the parent node is of typent:folder. Otherwise the node will be created with primary node typent:resource.
If the node to be created is nt:file, the actual file data will really be stored in the jcr:content child node of the new nt:file node whose primary node type is then set as nt:resource.
Example 1: Upload an image to a node named image below /content/page:
<form method="POST" action="/content/page" enctype="multipart/form-data"> <input type="file" name="image" /> <input type="Submit" /> </form>
Example 2: Upload a file as a node of type nt:file below /content/folder:
<form method="POST" action="/content/page" enctype="multipart/form-data"> <input type="file" name="*" /> <input type="hidden" name="*@TypeHint" value="nt:file" /> <input type="Submit" /> </form>
Assuming the user selected a file named myImage.jpg the uploaded file would be stored in an nt:file node at /content/folder/myImage.jpg.
Date properties¶
Parameters providing date/time values to be stored in JCR properties of type Date require special handling. The problem is that there are a number of formats to represent such date/time values. To account for this open-ended list of formats, the Sling Post Servlet supports configurability of the process of parsing strings into Calendar objects.
The Sling Post Servlet configuration property servlet.post.dateFormats takes a list of format strings which are used to setup java.text.SimpleDateFormat instances for parsing date/time string representations. A special format string ISO8601 is supported to indicate the string to be parsed as a JCR standard string representation of a Date property.
Only the latter supports storing the actual timezone offset. All the parsers leveraging java.text.SimpleDateFormat loose the given timezone and convert that just to the default timezone of the JRE (when creating the Calendar out of the Date, because java.lang.Date is not carrying any timezone information).
The default list of configured date/time parse pattern is:
- EEE MMM dd yyyy HH:mm:ss 'GMT'Z
- ISO8601, using the org.apache.jackrabbit.util.ISO8601 parser (±YYYY-MM-DDThh:mm:ss.SSSTZD)
- yyyy-MM-dd'T'HH:mm:ss.SSSZ
- yyyy-MM-dd'T'HH:mm:ss
- yyyy-MM-dd
- dd.MM.yyyy HH:mm:ss
- dd.MM.yyyy
Any date/time string parameter supplied is subject to the patterns in the configured order. The first pattern accepting the string and parsing it into a Date -- and thus a Calendar -- object is used. Therefore this list is best ordered in a most-stringent to least-stringent order.
Omitting Some Parameters¶
There may be times that you have forms which contain a lot of fields which you do not want to actually store in content. Such forms usually are created using some client-side GUI library which uses the fields for its own purposes. To be able to easily differentiate between real content to be actually stored and such control parameters, you may prefix the names of the fields destined for content with a dot-slash (./).
As soon as the SlingPostServlet encounters parameters prefixed with dot-slash, only those parameters are considered for content updates while all other parameters not prefixed are just ignored. In addition to dot-slash prefixed parameters, also parameters prefixed with dot-dot-slash (../) and slash (/) are considered in this situation.
For example, the following form only uses the first two fields for content update and ignores the rest:
<form method="POST" action="/content/page/first" enctype="multipart/form-data"> <input type="text" name="./title" /> <input type="text" name="../first/text" /> <input type="hidden" name="control0" /><!-- ignored --> <input type="hidden" name="control1" /><!-- ignored --> <input type="Submit" /> </form>
Because the SlingPostServlet encounters the ./title parameter, only parameters prefixed with dot-slash, dot-dot-slash and slash are considered for content update. In this case this would ./title and ../first/text while control0 and control1 are not prefixed and thus ignored.
Background: The name of the parameters used for content update are actually intended to be relative path names of the properties to modify. So in effect using the field name text is equivalent to ./text -- dot-slash meaning relative to the current node identified by the action attribute value for form tag -- or ../first/text if first is the name of the node to modify -- dot-dot-slash meaning relative to the parent node of the node identified by the action attribute value of the form tag.
In addition to the mechanism explained here, the following parameters are also ignored:
- Parameters whose name start with a colon (
:) are always ignored by the SlingPostServlet with respect to content update. The reason is that the prefixing colon is intended as a marker for SlingPostServlet control parameters. - The
charsetrequest parameter is also never written back because this parameter is used to convey the character encoding used to transport the request parameters. - Request parameters matching a regular expression supplied with the
servlet.post.ignorePatternconfiguration parameter are also ignored. By default this pattern isj_.*thus ignoring any request parameters with the prefixj_such asj_username. Those request parameters are generally used for authentication purposes and may hit the Sling POST Servlet in some situations.
Controlling Content Updates with @ Suffixes¶
Generally just creating forms with parameters and their values suffices it completely. Sometimes, though, you want to have more control on how the parameter values are actually stored in the properties. For example, you want to set a property to a default value if the user did provide an actual value. Or you might want to store a parameter explicitly with a given data type, such as numeric, boolean etc.
The SlingPostServlet provides such property control in the form of @ suffixed parameters, which are now presented.
The @ suffixed parameters are not used on their own but always in conjunction with a plain parameter. The part of the parameter name before the @ suffix is used in this case for correlation and must match exactly the name of the parameter to which the @ suffixed parameter belongs.
For example, the parameter width@TypeHint applies to the width parameter and the ./height@TypeHint parameter applies to the ./height parameter. As can be seen, the correlation between the parameters is a simple case-sensitive string comparison. That is the widht@TypeHint parameter would not apply to the ./width even though both parameters address the same property but they do not have a string match.
@TypeHint¶
Parameters with the @TypeHint suffix may be used to force storing the named parameter in a property with the given type. The value of the @TypeHint parameter, if applied to a parameter for a property, is the JCR property type name. If the @TypeHint parameter is applied to a field upload parameter, the value is used to indicate the JCR primary node type for the node into which the uploaded file is stored.
If the @TypeHint value ends with [], it indicates a multi-value property. A multi-value property is usually auto-detected if there are multiple values for the property (i.e. request parameter). But if only a single value is present in the request, the desired property type needs to be explicitly defined as multi-value by stating @TypeHint=<type>[].
Example: The following form sets the numeric width, the boolean checked, and the multi-valued hobbys (with 3 values to enter) properties:
<form method="POST" action="/content/page/first" enctype="multipart/form-data"> <input type="text" name="width" /> <input type="hidden" name="width@TypeHint" value="Long" /> <input type="checkbox" name="checked" /> <input type="hidden" name="checked@TypeHint" value="Boolean" /> <input type="text" name="hobbys"/> <input type="text" name="hobbys"/> <input type="text" name="hobbys"/> <input type="hidden" name="hobbys@TypeHint" value="String[]" /> <input type="Submit" /> </form>
In real applications you would need some JavaScript that allows to add/remove values, ie. add/remove inputs with the name "hobbys". Or a pure JavaScript based form post would be used, that gathers the properties to update programmatically, but the additional parameter hobbys@TypeHint=String[] would be the same.
The @TypeHint suffixed parameter is assumed to be single-valued. If the parameter has multiple values, only the first is actually used.
For multi-value properties, see also the @Patch option.
For more information on applying @TypeHint to a file upload parameter see the section on File Uploads above.
@DefaultValue¶
The @DefaultValue suffixed parameter may be provided to set a property to a default value should no value be provided in the actual parameters. Same as for normal parameters, the @DefaultValue parameter may have multiple values to create multi-valued properties.
Example: Set the text property to a default value if the user does not provide one:
<form method="POST" action="/content/page/first" enctype="multipart/form-data"> <input type="text" name="text" /> <input type="hidden" name="text@DefaultValue" value="--- Default Value ---" /> <input type="Submit" /> </form>
@UseDefaultWhenMissing¶
As described above, @DefaultValue only takes effect if no value is provided for a particular parameter. However, in some cases, such as HTML checkboxes, this isn't sufficient because the parameter isn't submitted at all. To handle this scenario, you can use the @UseDefaultWhenMissing suffixed parameter.
<form method="POST" action="/content/page/first" enctype="multipart/form-data"> <input name="queryIgnoreNoise" class="input" type="checkbox" value="true"/> <input type="hidden" name="queryIgnoreNoise@DefaultValue" value="false"/> <input type="hidden" name="queryIgnoreNoise@UseDefaultWhenMissing" value="true"/> </form>
@IgnoreBlanks¶
Sometimes a form client will supply empty parameter values resulting in content being created or modified. For example submitting this form:
<form method="POST" action="/content/page/first" enctype="multipart/form-data"> <input type="hidden" name="stringProperty@TypeHint" value="String[]"/> <input type="text" name="stringProperty" value="foo"/> <input type="text" name="stringProperty" value="bar"/> <input type="text" name="stringProperty" value=""/> </form>
will result in multi-value String property being set to [ "foo", "bar", "" ]. Notice the blank value.
Likewise submitting this form without a value entered:
<form method="POST" action="/content/page/first" enctype="multipart/form-data"> <input type="hidden" name="stringProperty@TypeHint" value="String"/> <input type="text" name="stringProperty" value=""/> </form>
will result in the single-value String property being set to an empty string.
To overcome this situation the @IgnoreBlanks suffix may be used to consider parameters with an empty string value to be ignored during processing. That is such parameter values would be treated as if they would not be supplied.
Adding
<input type="hidden" name="stringProperty@IgnoreBlanks" value="true"/>
to the above forms will cause the multi-value property be set to the two-element value [ "foo", "bar" ] and to not modify the property at all in the second single-value example.
@ValueFrom¶
In some situations, an HTML form with parameters may be reused to update content. But one or more form parameters may not comply with the names expected to be used for properties. In this case a parameter suffixed with @ValueFrom may be set containing the name of the parameter providing the actual data to be used.
Example: To set the property text from a form element supplied_text, you might use the following form:
<form method="POST" action="/content/page/first" enctype="multipart/form-data"> <input type="text" name="supplied_text" /> <input type="hidden" name="./text@ValueFrom" value="supplied_text" /> <input type="Submit" /> </form>
To prevent storing the additional parameters in the repository you might want to use the prefixing mechanism as shown in the example above, where the @ValueFrom parameter is prefixed and thus the supplied_text parameter is not used for property setting.
The @ValueFrom suffixed parameter is assumed to be single-valued. If the parameter has multiple values it is ignored completely.
The @ValueFrom suffixed parameter is also special in that there must not be a correlated parameter without a suffix. Thus have parameters text and text@ValueFrom may have unexpected results.
@Delete¶
Sometimes it may be required to not set a property to a specific value but to just remove it while processing the content update request. One such situation is a property filled from one or more checkboxes in an HTML form. If none of the checkboxes are checked, no parameter is actually submitted for these checkboxes. Hence the SlingPostServlet will not touch this property and effectively leave it untouched, while the natural reaction would have been to remove the property.
Here comes the @Delete suffixed parameter. This simply causes the indicated property be removed if it exists. If the property does not exist, nothing more happens. The actual value of the @Delete suffixed parameter does not care as long as the parameter is submitted.
Example: To ensure the color property is actually removed if no color has been selected, you might use the following form:
<form method="POST" action="/content/page/first" enctype="multipart/form-data"> <input type="checkbox" name="color" value="red" /> <input type="checkbox" name="color" value="green" /> <input type="checkbox" name="color" value="blue" /> <input type="hidden" name="color@Delete" value="delete text" /><!-- actual value is ignored --> <input type="Submit" /> </form>
The @Delete suffixed parameter is also special in that there need not be a correlated parameter without a suffix. If both -- a parameters text and text@Delete are set, the text property is first deleted and then filled with the new content.
The @Delete suffixed parameter in fact calls for a sub-operation, which is executed after the node addressed by the request URL is created (if needed) but before any other tasks of content creation and modification are done. Any item -- this may be a property or a node, actually -- addressed by the @Delete suffixed parameter is just removed if it exists. If the item does not exist, nothing happens.
@MoveFrom¶
Now, that your bright and shiny content management application has great Flash-based file upload feature you will want to be able to use the pre-uploaded files for your content with the same request as when you upload other content. For example you might have a node storing some text and an illustration you uploaded as an image file.
To support this kind of functionality, the @MoveFrom suffixed parameter may be set to the repository path of the node to where you uploaded the image file.
Example: Your Flash-based file upload stored the file on the server at /tmp/upload/123. You now want to store this file along with a title and a text in a newly created node. The following form will be your friend:
<!-- trailing slash generates a name for the new node --> <form method="POST" action="/content/page/" enctype="multipart/form-data"> <input type="hidden" name="image@MoveFrom" value="/tmp/upload/123" /> <input type="text" name="title" /> <input type="text" name="text" /> <input type="Submit" /> </form>
If there exists no repository item at the indicated path, nothing is done. If the item indicated by the @MoveFrom suffixed parameter already exists, it is replaced by the item addressed by the parameter value -- unless of course there is no item at the named location.
The @MoveFrom suffixed parameter is assumed to be single-valued. If the parameter has multiple values it is ignored completely.
The @MoveFrom suffixed parameter is also special in that there must not be a correlated parameter without a suffix. Thus have parameters text and text@MoveFrom may have unexpected results.
The @MoveFrom suffixed parameter in fact calls for a sub-operation, which is executed after the @Delete sub operation but before any other tasks of content creation and modification are done.
@CopyFrom¶
Similar to the @MoveFrom suffix exists a @CopyFrom suffix. The latter works exactly the same as the former except that the item addressed by the parameter value is not moved but just copied.
Example: Your Flash-based file upload stored the file on the server at /tmp/upload/123. You now want to store this file along with a title and a text in a newly created node. The following form may be your friend:
<!-- trailing slash generates a name for the new node --> <form method="POST" action="/content/page/" enctype="multipart/form-data"> <input type="hidden" name="image@CopyFrom" value="/tmp/upload/123" /> <input type="text" name="title" /> <input type="text" name="text" /> <input type="Submit" /> </form>
If there exists no repository item at the indicated path, nothing is done. If the item indicated by the @CopyFrom suffixed parameter already exists, it is replaced by the item addressed by the parameter value -- unless of course there is no item at the named location.
The @CopyFrom suffixed parameter is assumed to be single-valued. If the parameter has multiple values it is ignored completely.
The @CopyFrom suffixed parameter is also special in that there must not be a correlated parameter without a suffix. Thus have parameters text and text@CopyFrom may have unexpected results.
The @CopyFrom suffixed parameter in fact calls for a sub-operation, which is executed after the @MoveFrom sub operation but before any other tasks of content creation and modification are done.
@Patch¶
When modifying multi-value properties, the @Patch suffix can be used to just add + or remove - individual values without overwriting the full array. This allows to change the array without knowing the current values.
For example, imagine a multi-value string property that stores tags or keywords. To both add a tag "cool" and remove "boring" from the list:
<form method="POST" action="/content/page/first" enctype="multipart/form-data"> <input type="hidden" name="tags@TypeHint" value="String[]" /> <input type="hidden" name="tags@Patch" value="true" /> <input type="text" name="tags" value="+cool"/> <input type="text" name="tags" value="-boring"/> <input type="Submit" /> </form>
The array will be treated like a set: when adding a value, it will only be added once if it does not exist yet; when removing a value, all occurrences of it will be removed. For values not affected by the add or remove operations, nothing changes. An existing array with duplicate entries will not automatically be converted into a set.
The format for an individual parameter value is <operation><value>. If there is no or no valid operation given, this value will be ignored.
Operation + will add the <value> to the array if it is not part of it yet.
Operation - will remove all occurrences of <value> from the array.
The value of the @Patch suffixed parameter is irrelevant, it can be empty (example above uses true for clarity).
All types should be supported via @TypeHint, but it needs to indicate a multi-value property, ending with [].
Algorithm for Node Name Creation¶
If request is posted with an URL ending in slash / or slash-star /*, the SlingPostServlet derives a name for the node to be created upon the request applying the following algorithm:
- If a
:nameparameter is supplied, the (first) value of this parameter is used unmodified as the name for the new node. If the name is illegally formed with respect to JCR name requirements, an exception will be thrown when trying to create the node. The assumption with the:nameparameter is, that the caller knows what he (or she) is supplying and should get the exact result if possible. - Otherwise if a
:nameHintparameter is supplied, the (first) value of this parameter is used to generate the node name. A name filtering is applied to this hint to ensure a valid JCR node name. - Otherwise a series of request parameters supplied to set content is inspected for a possible name. The list of the names of these parameter is configurable with the SlingPostServlet and defaults to
[ title, jcr:title, name, description, jcr:description, abstract ](refs.-title-jcr-title-name-description-jcr-description-abstract.path). The first request parameter with a non-empty value is used and filtered to get the valid JCR name. - Otherwise an ever increasing auto generated number is used. Filtering is also applied to this numeric name.
The filtering algorithm to create a valid name of the hints from above steps (except the first) works as follows:
- Convert the proposed name to all lower case.
- Replace all characters not in the range [0..9a..z*] by a single underscore
_. - If the name starts with a digit prepend an underscore. Technically names with leading digits are valid, but they present major issues when using such names in JCR XPath expressions. The algorithm takes care to not create names with two or more consecutive underscore characters.
- Finally the name is cut to a configurable maximum length (default is 20 characters).
For example the :nameHint value A quick brown Fox ... is filtered to become a_quick_brown_fox_.
After generating and filtering the name it is further guaranteed that the name is unique: If a node of the same name as just generated from the algorithm already exists below the same parent node a numeric index is appended to the new node name to make it unique.
Response Status¶
The modification operation has the following status responses:
| Status | Explanation |
|---|---|
| 200/OK | An existing node has been updated with content |
| 201/CREATED | A new node has been created and filled with content |
| 500/INTERNAL SERVER ERROR | Some exception, for example a RepositoryException, occurred while processing the request |
Content Removal¶
To remove existing content just address the item to be removed and set the :operation parameter to delete. For example the following command line removes the /content/sample page:
$ curl -F":operation=delete" http://host/content/sample
Response Status¶
The delete operation has the following status responses:
| Status | Explanation |
|---|---|
| 200/OK | The resource (and all its descendants) has been removed |
| 404/NOT FOUND | The request URL does not address an existing repository item |
| 500/INTERNAL SERVER ERROR | Some exception, for example a RepositoryException, occurred while processing the request |
Deleting Multiple Items¶
By using the :applyTo request parameter it is possible to remove multiple items in one single request. Deleting items in this way leaves you with less control, though. In addition, if a single item removal fails, no item at all is removed.
When specifying the item(s) to be removed with the :applyTo parameter, the request resource is left untouched (unless of course if listed in the :applyTo parameter) and only used to resolve any relative paths in the :applyTo parameter.
To remove the /content/page1 and /content/page2 nodes, for example, you might use the following command line:
$ curl -F":operation=delete" -F":applyTo=/content/page1" \ -F":applyTo=/content/page2" http://host/content/sample
Using a trailing star in the :applyTo parameter (as mentioned before), you can remove all the children of the /content node, for example, as follows:
$ curl -F":operation=delete" -F":applyTo=/content/*" http://host/content/sample
If any resource listed in the :applyTo parameter does not exist, it is silently ignored.
Response Status¶
The delete operation applied to multiple resources has the following status responses:
| Status | Explanation |
|---|---|
| 200/OK | All requested and existing resources have been removed |
| 500/INTERNAL SERVER ERROR | Some exception, for example a RepositoryException, occurred while processing the request |
Copying Content¶
To copy existing content to a new location, the copy operation is specified. This operation copies the item addressed by the request URL to a new location indicated by the :dest parameter. The :dest parameter is the absolute or relative path to which the resource is copied. If the path is relative it is assumed to be below the same parent as the request resource. If it is terminated with a / character the request resource is copied to an item of the same name under the destination path.
To illustrate the :dest parameter handling, lets look at a few examples. All examples are based on addressing the /content/sample item:
:dest Parameter |
Destination Absolute Path |
|---|---|
/content/newSample |
/content/newSample |
different/newSample |
/content/different/newSample |
/content/different/ |
/content/different/sample |
different/ |
/content/different/sample |
If an item already exists at the location derived from the :dest parameter, the copy operation fails unless the :replace parameter is set to true (case is ignored when checking the parameter value).
Response Status¶
The copy operation has the following status responses:
| Status | Explanation |
|---|---|
| 200/OK | The node has been copied to the new location replacing an existing item at the destination |
| 201/CREATED | The node has been copied to the new location creating a new item at the destination |
| 404/NOT FOUND | The request URL does not address an existing repository item |
| 412/PRECONDITION FAILED | An item already exists at the destination and the :replace parameter is not set to true |
| 500/INTERNAL SERVER ERROR | Some exception, for example a RepositoryException, occurred while processing the request |
Copying Multiple Items¶
By using the :applyTo request parameter it is possible to copy multiple items in one single request. Copying items in this way leaves you with less control, though. In addition, if a single item copy fails, no item at all is copied.
When specifying the item(s) to be copied with the :applyTo parameter, the request resource is left untouched (unless of course if listed in the :applyTo parameter) and only used to resolve any relative paths in the :applyTo parameter.
To copy the /content/page1 and /content/page2 nodes to /content/target, for example, use:
$ curl -F":operation=copy" -F":applyTo=/content/page1" -F":applyTo=/content/page2" \ -F":dest=/content/target/" http://host/content/sample
Please note the trailing slash character (/) in the value of the :dest parameter. This is required for multi-item copy operations using the :applyTo parameter. The copied items are created below the node indicated by the :dest.
Using a trailing star in the :applyTo parameter (as mentioned before), you can copy all the children of the /content node, for example, as follows:
$ curl -F":operation=copy" -F":applyTo=/content/*" -F":dest=/content/target/" \ http://host/content/sample
If any resource listed in the :applyTo parameter does not exist, it is silently ignored. Any item already existing at the copy destination whose name is the same as the name of an item to be copied is silently overwritten with the source item.
Response Status¶
The copy operation applied to multiple resources has the following status responses:
| Status | Explanation |
|---|---|
| 200/OK | All requested and existing resources have been copied |
| 412/PRECONDITION FAILED | The node indicated by the :dest parameter does not exist |
| 500/INTERNAL SERVER ERROR | Some exception, for example a RepositoryException, occurred while processing the request. This status is also set if the :dest parameter value does not have a trailing slash character. |
Moving Content¶
To move existing content to a new location, the move operation is specified. This operation moves the item addressed by the request URL to a new location indicated by the :dest parameter. The :dest parameter is the absolute or relative path to which the resource is moved. If the path is relative it is assumed to be below the same parent as the request resource. If it is terminated with a / character the request resource is moved to an item of the same name under the destination path.
To illustrate the :dest parameter handling, lets look at a few examples. All examples are based on addressing the /content/sample item:
:dest Parameter |
Destination Absolute Path |
|---|---|
/content/newSample |
/content/newSample |
different/newSample |
/content/different/newSample |
/content/different/ |
/content/different/sample |
different/ |
/content/different/sample |
If an item already exists at the location derived from the :dest parameter, the move operation fails unless the :replace parameter is set to true (case is ignored when checking the parameter value).
Response Status¶
The move operation has the following status responses:
| Status | Explanation |
|---|---|
| 200/OK | The node has been moved to the new location replacing an existing item at the destination |
| 201/CREATED | The node has been moved to the new location creating a new item at the destination |
| 404/NOT FOUND | The request URL does not address an existing repository item |
| 412/PRECONDITION FAILED | An item already exists at the destination and the :replace parameter is not set to true |
| 500/INTERNAL SERVER ERROR | Some exception, for example a RepositoryException, occurred while processing the request |
Moving Multiple Items¶
By using the :applyTo request parameter it is possible to move multiple items in one single request. Moving items in this way leaves you with less control, though. In addition, if a single item move fails, no item at all is moved.
When specifying the item(s) to be moved with the :applyTo parameter, the request resource is left untouched (unless of course if listed in the :applyTo parameter) and only used to resolve any relative paths in the :applyTo parameter.
To for example move the /content/page1 and /content/page2 nodes to /content/target, you might use the following command line:
$ curl -F":operation=move" -F":applyTo=/content/page1" -F":applyTo=/content/page2" \ -F":dest=/content/target/" http://host/content/sample
Please note the trailing slash character (/) in the value of the :dest parameter. This is required for multi-item move operations using the :applyTo parameter. The moved items are created below the node indicated by the :dest.
Using a trailing star in the :applyTo parameter (as mentioned before), you can move all the children of the /content node, for example, as follows:
$ curl -F":operation=move" -F":applyTo=/content/*" -F":dest=/content/target/" \ http://host/content/sample
If any resource listed in the :applyTo parameter does not exist, it is silently ignored. Any item already existing at the move destination whose name is the same as the name of an item to be moved is silently overwritten with the source item.
Response Status¶
The move operation applied to multiple resources has the following status responses:
| Status | Explanation |
|---|---|
| 200/OK | All requested and existing resources have been moved |
| 412/PRECONDITION FAILED | The node indicated by the :dest parameter does not exist |
| 500/INTERNAL SERVER ERROR | Some exception, for example a RepositoryException, occurred while processing the request. This status is also set if the :dest parameter value does not have a trailing slash character. |
Importing Content Structures¶
To import content structures just address the parent item to import into and set the :operation parameter to import.
The optional name of the root node of the imported content may optionally be supplied using the Algorithm for Node Name Creation.
Other parameters for the import operation:
| Parameter | Required | Default value | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
:contentType |
true |
The :contentType value specifies the type of content being imported. Possible values are: xml, jcr.xml, json, jar, zip |
|
:content |
false |
The :content value specifies content string to import. The format of the import content is the same as is used by the jcr.contentloader bundle. This parameter is required if the :contentFile parameter is not supplied. |
|
:contentFile |
false |
The :contentFile value specifies a file uploaded for import. The format of the import content is the same as is used by the jcr.contentloader bundle. This parameter is required if the :content parameter is not supplied. |
|
:checkin |
false |
false | The :checkin value specifies whether versionable nodes should be checked in during the import. |
:autoCheckout |
false |
false | The :autoCheckout value specifies whether versionable nodes should be checked out when necessary during the import. |
:replace |
false |
false | The :replace value specifies whether the import should replace any existing nodes at the same path. Note: When true, the existing nodes will be deleted and a new node is created in the same place. |
:replaceProperties |
false |
false | The :replaceProperties value specifies whether the import should replace properties if they already exist. |
For example the following command line imports the /content/sample page:
$ curl -F":operation=import" -F":contentType=json" -F":name=sample" \ -F':content={ "jcr:primaryType": "nt:unstructured", "propOne" : "propOneValue", "childOne" : { "childPropOne" : true } }' \ http://host/content
For example the following command line imports the /content/sample page without the optional name parameter:
$ curl -F":operation=import" -F":contentType=json" -F':content={ "sample" : {"propOne" : "propOneValue", "childOne" : { "childPropOne" : true } } }' \ http://host/content
For example the following form imports the /content/sample page:
<form method="POST" action="/content" enctype="multipart/form-data"> <input type="hidden" name=":operation" value="import" /> <input type="hidden" name=":contentType" value="json" /> <input type="hidden" name=":nameHint" value="sample" /> <input type="text" name=":content" value="{ "jcr:primaryType" : "nt:unstructured" , "propOne" : "propOneValue", "childOne" : { "childPropOne" : true } }" /> <input type="Submit" /> </form>
For example the following form imports content from a file upload:
<form method="POST" action="/content" enctype="multipart/form-data"> <input type="hidden" name=":operation" value="import" /> <input type="hidden" name=":contentType" value="json" /> <input type="hidden" name=":nameHint" value="sample" /> <input type="file" name=":contentFile" /> <input type="Submit" /> </form>
Response Status¶
The move operation applied to multiple resources has the following status responses:
| Status | Explanation |
|---|---|
| 200/OK | All requested content has been imported |
| 404/NOT FOUND | The target parent node does not exist |
| 412/PRECONDITION FAILED | One or more of the required parameters does not exist |
| 500/INTERNAL SERVER ERROR | Some exception, for example a RepositoryException, occurred while processing the request. This status is also set if the ContentImporter service is missing. |
Null Operation¶
Sometimes it is useful to explicitly request that nothing is to be done. The SlingPostServlet now provides such an operation under the name nop. Apart from doing nothing, the nop operations sets the response status to either the default 200/OK or to any status requested by the :nopstatus request parameter.
The :nopstatus request parameter must be an integral number in the range [ 100 .. 999 ]. If the parameter value cannot be parsed to an integer or the value is outside of this range, the default status 200/OK is still set.
Response Status¶
The null operation sets a default status or the status requested by the :nopstatus request parameter.
| Status | Explanation |
|---|---|
| 200/OK | Default status set if :nopstatus parameter is not set or does not have a valid value |
The status as requested by the :nopstatus parameter |
Special Parameters¶
Some parameters have special significance for the complete processing of the SlingPostServlet or are used by multiple operations. This section summarizes these parameters:
:order¶
Child nodes may be ordered if the primary node type of their common parent node is defined as having orderable child nodes. To employ such ordering, the content creation/modification, move and copy operations support the :order parameter which apply child node ordering amongst its siblings of the target node.
The :order parameter may have the following values:
| Value | Description |
|---|---|
first |
Place the target node as the first amongst its siblings |
last |
Place the target node as the last amongst its siblings |
before *xyz* |
Place the target node immediately before the sibling whose name is xyz |
after *xyz* |
Place the target node immediately after the sibling whose name is xyz |
| numeric | Place the target node at the indicated numeric place amongst its siblings where 0 is equivalent to first and 1 means the second place |
Note that simple content reordering can be requested without applying any other operations. This is easiest done by placing a request to the resource to be reordered and just setting the :order parameter. For example to order the /content/sample/page5 resource above its sibling resource /content/sample/other a simple request
$ curl -F":order=before other" http://host/content/sample/page5
does the trick. To be redirected after the reodering, the :redirect parameter may optionally also be specified.
:redirect¶
Instructs the SlingPostServlet to redirect the client to the indicated location if the operation succeeds. That is the response status is set to 302/FOUND and the Location header is set to the value of the :redirect parameter.
:status¶
By default the SlingPostServlet sets response status according to the status of the operation executed. In some cases, it may be desirable to not have the real status codes (e.g. 404 or 505) but a normal 200/OK to trick the client browser into displaying the response content generated by the SlingPostServlet.
To not send the actual response status back to the client, the :status request parameter should be set to browser. If this parameter is not set, is empty, is set to standard or to any other value, the actual status code is sent back to the client.
Response format¶
The SlingPostServlet produces a basic HTTP response body, listing the response status, what changes have been made, and other meta-data about the result of the POST request.
The format of this response is either HTML or JSON (JSON support introduced with SLING-1336). SlingPostServlet determines which format to use by examining the Accept header of the incoming request. If the client has specified a preference for the media type "application/json", the JSON format is used, otherwise HTML is returned. The Accept header can be overridden (and simulated) by posting a :http-equiv-accept field, which should have the same format as the Accept header.
Examples:
- Accept: text/html,application/xhtml+xml,application/xml;q=0.9,/;q=0.8
- Accept: application/json,/;q=0.9
In example #1, SlingPostServlet will return HTML, since the client has specified a preference for text/html. In example #2, SlingPostServlet will return JSON.
See RFC 2616, section 14.1 for information on the HTTP Accept header.
Versionable Node Support¶
The modify (default), delete, move, and copy operations of the SlingPostServlet support JCR Versionable Nodes. By default, when a node needs to be checked out for a modification to occur, it will be checked out and any nodes the operation checks out will be checked in upon completion of the request. Newly created versionable nodes (or non-versionable nodes made versionable by adding the mix:versionable mixin) will be left in their default, checked out state.
This default behavior can be modified either globally (i.e. for all requests) or on a per-request basis. The global behavior is changed through OSGi ConfigAdmin using these three properties of the PID org.apache.sling.servlets.post.impl.SlingPostServlet:
servlet.post.checkinNewVersionableNodesservlet.post.autoCheckoutservlet.post.autoCheckin
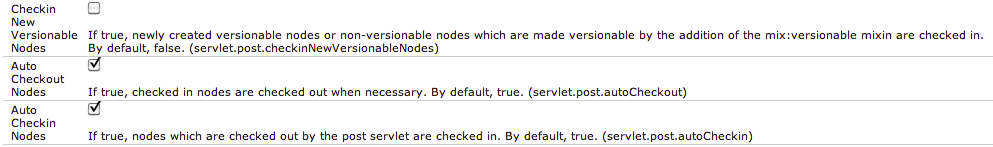
On a per-request basis, these request parameters can be used:
:checkinNewVersionableNodes:autoCheckout:autoCheckin
Checkout and Check In changes will be reflected in the ChangeLog portion of the response.
Extending the SlingPostServlet¶
Additional POST operations¶
OSGi services of the org.apache.sling.servlets.post.PostOperation type can be used to implement new POST operations.
Such services must have a sling.post.operation service registration property set to the name of the operation. This name is used as the value of the :operation parameter of POST requests to select the extended operation.
Before version 2.1.2 of the org.apache.sling.servlets.post bundle, such additional operations were implemented by the org.apache.sling.servlets.post.SlingPostOperation interface, which is now deprecated but still supported via a bridge. See SLING-1725 for details and discussions about this change.
Two examples (old and new style) of additional POST operations are found in the test-services module, with the corresponding test code in the integration-tests module.
SlingPostProcessor¶
OSGi services of the org.apache.sling.servlets.post.SlingPostOperation type can be used to post process PostOperations. They are called after the operation has performed its changes but before the changes are persisted (via commit). All registered SlingPostProcessors are always called in the reverse order of their service ranking (i.e. the one with the highest service ranking first).
A SlingPostProcessor may perform additional changes or revert previous ones. It is important that the SlingPostProcessor does not commit its changes but rather only performs the changes in the transient space (with the resource resolver bound to the current request) and in addition reports the changes through the 2nd parameter of the method process(SlingHttpServletRequest, List<Modification>).
Two examples of SlingPostProcessors are found in the test-services module, with the corresponding test code in the integration-tests module.
