Apache Felix JAAS Support
- The Problem
- Usage
- LoginModule registration
- LoginContext creation patterns
- LoginContextFactory Mode
- Configuration SPI with Default Policy Mode
- Replace Global Configuration Mode
- Modified Boot Classpath Mode
- JAAS Configuration SPI Settings
- WebConsole Plugin
- Resources
Apache Felix JAAS support aims to simplify usage of JAAS in OSGi.
It supports following features
- It can work both in Standalone and AppServer deployments i.e. in those environment where global JAAS configuration might be used by other applications and our usage of JAAS should not affect them
- It enables usage of OSGi Configuration support to dynamically configure the login modules.
- It allows LoginModule instances to be created via factories registered in OSGi Service Registry
- It does not require the client to depend on any OSGi API
- It works well with the dynamic nature of the OSGi env
- Implementation depends only on Core OSGi API and ConfigAdmin (RFC 104)
The Problem¶
The basic problem when using JAAS in OSGi is that it creates the LoginModule instance using reflection. This poses problem in OSGi env as the client bundle does not have the visibility of all the required LoginModule classes.
A typical use of JAAS login looks like below
// let the LoginContext instantiate a new Subject LoginContext lc = new LoginContext("myApp"); lc.login();
In this mode the LoginContext would access the global JAAS Configuration internally via Configuration.getConfiguration().
It would then instantiate the LoginModule instance based on the configuration value. It uses the Thread Context ClassLoader (TCCL)
to create the instance. This approach fails to work when used in OSGi
- The Thread Context ClassLoader is not defined in general in an OSGi context. It can and has to be set by the caller and OSGi cannot generally enforce that.
- Instantiating a LoginModule generally requires access to internal implementation classes, by exporting these classes an implementing bundle would break its encapsulation.
- Even if an implementation class was exported, importing this class in a consumer bundle would bind it to the specific implementation package provided, which violates the principle of loose coupling.
Usage¶
The JAAS support involves following parts
- LoginModule Registration - Mechanism by which LoginModule is registered with a given
realm. - LoginContext Creation - Refers to the client code which constructs the LoginContext and then perform login operation
In section below we would first provide details on various ways by which a LoginModule would be configured so that
it can participate in JAAS flow and then about various ways in which the client code can invoke the JAAS logic
LoginModule registration¶
The login modules can be registered via two mechanism
- OSGi Configuration - LoginModule are registered via OSGi configuration
- LoginModuleFactory - LoginModule are registered with the OSGi ServiceRegistry via
LoginModuleFactory
A - OSGi Configuration¶
LoginModules can also be configured via configuration which is somewhat similar to the file based configuration. It consist of two parts
- Information around which bundle provides a specific LoginModule module
- Configuration required to be passed to that LoginModule
Manifest Header Entry¶
Any bundle which provides a LoginModule class needs to provide this information via Jaas-ModuleClass manifest header.
<Jaas-ModuleClass>org.apache.felix.example.jaas.config.internal.SampleConfigLoginModule</Jaas-ModuleClass>
Configuration¶
JAAS module depends on OSGi Configuration for managing the LoginModule configuration. The configuration factory PID is
org.apache.felix.jaas.Configuration.factory.It provides the required metatype descriptor thus enabling configuration
via "Configuration" tab of Felix WebConsole

Configuration properties
jaas.classname- Fully qualified name of the LoginModule classjaas.controlFlag- LoginControlFlag to use like required, optional, requisite, sufficient. Default is set to requiredjaas.realmName- JAAS Realm name. If specified then LoginModule would be registered against given realm otherwise it is bound to a 'other' realmjaas.ranking- Ranking for the LoginModule. It would be used to order the various login modules. The entries are sorted in a descending order (i.e. higher value ranked configurations come first)
For an example refer to Sample Configuration. It configures a SampleConfigLoginModule for sample realm
B - LoginModuleFactory¶
Any bundle which want to provide a LoginModule implementation would need to provide a factory service which implements the LoginModuleFactory interface. The factory needs to be registeredwith following optional properties
jaas.controlFlag- LoginControlFlag to use like required, optional, requisite, sufficient. Default is set to requiredjaas.realmName- JAAS Realm name. If specified then LoginModule would be registered against given realm otherwise it is bound to a 'other' realm.service.ranking- Ranking for the LoginModule. It would be used to order the various login modules.
Interface
/** * A factory for creating {@link LoginModule} instances. */ public interface LoginModuleFactory { /** * Property name specifying whether or not a <code>LoginModule</code> is * REQUIRED, REQUISITE, SUFFICIENT or OPTIONAL. Refer to {@link javax.security.auth.login.Configuration} * for more details around the meaning of these flags * * By default the value is set to REQUIRED */ String JAAS_CONTROL_FLAG = "jaas.controlFlag"; /** * Property name specifying the Realm name (or application name) against which the * LoginModule would be registered. * * <p>If no realm name is provided then LoginModule would registered with a default realm * as configured */ String JAAS_REALM_NAME = "jaas.realmName"; /** * Creates the LoginModule instance * @return loginModule instance */ LoginModule createLoginModule(); }
Refer to JdbcLoginModuleFactory for one example of its usage. It constructs a JdbcLoginModule based on the configuration and passes on the datasource.
LoginContext creation patterns¶
There are various ways through which a JAAS Client can invoke the JAAS login.
LoginContextFactory Mode¶
In this mode the client logic obtains a reference to the org.apache.felix.jaas.LoginContextFactory service
and then creates a LoginContext instance
:java LoginContextFactory loginContextFactory = ... CallbackHandler handler = ...; Subject subject = new Subject(); try { LoginContext lc = loginContextFactory.createLoginContext("sample",subject,handler); lc.login(); ... } catch (LoginException e) { handleAuthenticationFailure(e); }
Refer to FactoryDemoServlet for an example. Following points to be noted for this usage pattern
- Client code needs to depend on Apache Felix JAAS Support API
- No need to manage Thread Context Classloader while invoking
LoginContext - No need to import LoginModule related packages
Configuration SPI with Default Policy Mode¶
In this mode the client logic explicitly fetch the JAAS Configuration and then pass it on to the LoginContext. In this
mode the JAAS Configuration Policy is set to Default.
CallbackHandler handler = ...; Subject subject = new Subject(); final ClassLoader cl = Thread.currentThread().getContextClassLoader(); try { Configuration config = Configuration.getInstance( 'JavaLoginConfig', //Algorithm name null, //Extra params to be passed. For this impl its null 'FelixJaasProvider' //Name of the config provider ); Thread.currentThread().setContextClassLoader(getClass().getClassLoader()); LoginContext lc = new LoginContext("sample", subject, handler, config); lc.login(); ... } finally { Thread.currentThread().setContextClassLoader(cl); }
In above flow the Configuration instance is explicitly fetched and passed on to the
Refer to TCCLDemoServlet for an example. Following points to be noted for this usage pattern
- Client code needs to be aware of the name of the config provider.
- Client bundle would need to have an import for package
org.apache.felix.jaas.boot. Refer to Boot classpath section for more details - Global configuration is not modified so other users of JAAS are not affected
Replace Global Configuration Mode¶
In this mode the JAAS bundle would replace the Global configuration through Configuration.setConfiguration call. In this
mode the client code would use the normal LoginContext creation and the JAAS Configuration Policy
is set to Replace Global Configuration.
final ClassLoader cl = Thread.currentThread().getContextClassLoader(); try { Thread.currentThread().setContextClassLoader(getClass().getClassLoader()); // let the LoginContext instantiate a new Subject LoginContext lc = new LoginContext("appName"); lc.login(); } finally { Thread.currentThread().setContextClassLoader(cl); }
Following points need to be considered this mode
- Client code is not aware of the provider name
- Client bundle would need to have an import for package
org.apache.felix.jaas.boot. Refer to Boot classpath section for more details - Global configuration is modified. So it might cause issue while running in co deployed scenarios like Application Server.
Refer to GlobalConfigDemoServlet for an example
Modified Boot Classpath Mode¶
In previous modes (except the LoginContextFactory mode) the client code needs to switch the Thread Context Classloader (TCCL).
This is due the way JAAS logic instantiates the LoginModule. The Felix JAAS Support provides a ProxyLoginModule which
takes care of routing the LoginModule calls properly. However for this class to be visible to JAAS logic one of the
two approaches can be used
Manage TCCL Explicitly
The client bundle would need to
- Have an explicit import for
org.apache.felix.jaas.bootpackage and - Manage TCCL explicitly which making JAAS related calls.
final Thread current = Thread.currentThread(); final ClassLoader orig = current.getContextClassLoader(); try { current.setContextClassLoader(getClass().getClassLoader()); loginContext = new LoginContext(appName, subject,callbackHandler, config);
} finally{ current.setContextClassLoader(orig); }
Note that in above flow the TCCL is managed explicitly
Modify Boot Classpath
Another way would involve modifying the boot classpath.
- Place the
org.apache.felix.jaas-xxx-boot.jarin the boot classpath via-Xbootclasspath:bootclasspathoption - Make the
org.apache.felix.jaas.bootpart of boot delegation listLoginContext lc = new LoginContext("sample", subject, handler); lc.login();
Note that in above code we do not have to manage TCCL and neither add an import to org.apache.felix.jaas.boot package
Refer to BootClasspathDemoServlet for code sample
JAAS Configuration SPI Settings¶
There are various ways in which LoginContext can be created depending on the usage mode. The JAAS support exposes following properties
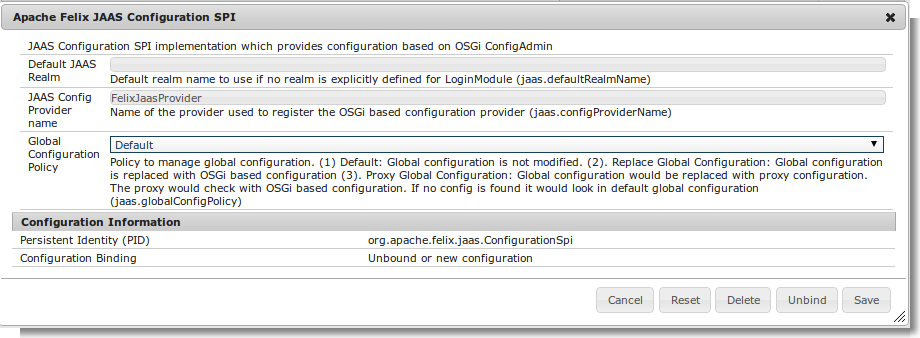
Default JAAS Realm- Name of the realm to use in case a LoginModule does not provide an explicit realmName. This is useful for single application mode where all LoginModule in an OSGi container are to be used. Usage of realm help in global settings because same config file is used to capture settings for all applications running on same JVMJAAS Config Provider name- Name against which the Configuration SPI provider should registerConfiguration Policy- This would be explained in next sectionDefault- Global configuration is not touched. Client code are expected to use the Configuration Spi modeReplace Global Configuration- In this the global configuration is replaced with OSGi configuration. Client code need not perform any special configuration handling. At most they need to switch the Thread Context ClassloaderProxy Global Configuration- Similar to previous one but it saves the default configuration and does a fallback check on that also. This should minimize any disruption in shared mode
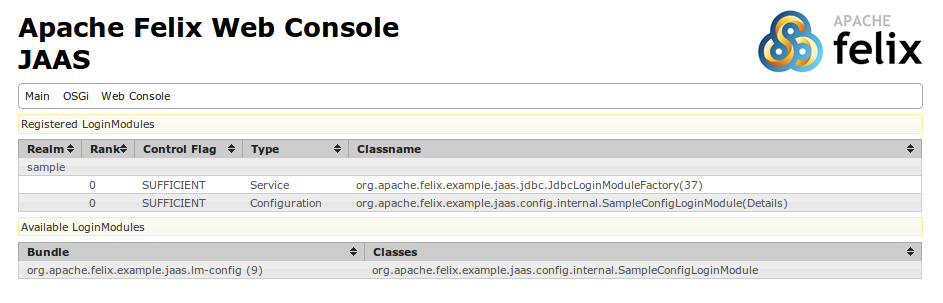
WebConsole Plugin¶
The runtime JAAS realm is exposed via a WebConsole Plugin.