
The Gremlin Console
In "The First Five Minutes" of the Apache TinkerPop tutorial on how to get started wth TinkerPop and graphs, the importance of the Gremlin Console was introduced. This tutorial further explores the usage of the console in the daily work of Gremlin developers delving more deeply into the details of its operations and expanding upon the basic usage guide in the reference documentation.

|
Important
|
This tutorial assumes that the Gremlin Console is installed and that you have some familiarity with Gremlin in general. Please be sure to read the Getting Started tutorial prior to proceeding further with this one. |
The Gremlin Console serves a variety of use cases that can meet the needs of different types of Gremlin users. This tutorial explores the features of the Gremlin Console through a number of these different use cases to hopefully inspire you to new levels of usage. While a use case may not fit your needs, you may well find it worthwhile to read, as it is possible that a "feature" will be discussed that may be useful to you.
The following points summarize the key features discussed in each use case:
-
-
Introducing the toy graphs
-
Finding help for commands
-
-
-
Static importing of common methods
-
-
-
Deciding when to use the def keyword
Use Case: A Learning Tool
 You are a new user of Apache TinkerPop and perhaps new to graphs as well.
You’re trying to get familiar with how Gremlin works and how it might fit into your project. You want some "quick
wins" with Gremlin and aim to conceptually prove that the TinkerPop stack is a good direction to go.
You are a new user of Apache TinkerPop and perhaps new to graphs as well.
You’re trying to get familiar with how Gremlin works and how it might fit into your project. You want some "quick
wins" with Gremlin and aim to conceptually prove that the TinkerPop stack is a good direction to go.
It cannot be emphasized enough just how important the Gremlin Console is to new users. The interactive nature of a REPL makes it possible to quickly try some Gremlin code and get some notion of success or failure without the longer process of build tools (e.g. Maven), IDEs, compilation, and application execution. The faster that you can iterate through versions of your Gremlin code, the faster you can advance your knowledge.
As a new user, your best way to learn is to try Gremlin with a graph already packaged with the console: TinkerGraph. TinkerGraph is an in-memory graph database that is easy to use and does not have a lot of configuration options to be concerned with. You can create an empty TinkerGraph as follows:
gremlin> graph = TinkerGraph.open() //(1)
==>tinkergraph[vertices:0 edges:0]
gremlin> g = graph.traversal() //(2)
==>graphtraversalsource[tinkergraph[vertices:0 edges:0], standard]-
Creates the
Graphinstance that is the API to the structure of the graph. -
Creates the
TraversalSourcewhich is the API for processing or traversing thatGraph.
|
Important
|
TinkerPop recommends creating the TraversalSource once and re-using it as necessary in your application.
|
Now that you have an empty TinkerGraph instance, you could load a sample of your data and get started with some
traversals. Of course, you might also try one of the "toy" graphs (i.e. graphs with sample data) that TinkerPop
packages with the console through the TinkerFactory. TinkerFactory has a number of static methods that can be
called to create these standard TinkerGraph instances. They are "standard" in the sense that they are typically used
for all TinkerPop examples and test cases.
-
createClassic()- The original TinkerPop 2.x toy graph (diagram). -
createModern()- The TinkerPop 3.x representation of the "classic" graph, where the main difference is that vertex labels are defined and the "weight" edge property is adoublerather than afloat(diagram). -
createTheCrew()- A graph that demonstrates usage of the new structural features of TinkerPop 3.x (as compared to 2.x) such as vertex properties and multi-properties (diagram).
gremlin> graph = TinkerFactory.createModern()
==>tinkergraph[vertices:6 edges:6]
gremlin> g = graph.traversal()
==>graphtraversalsource[tinkergraph[vertices:6 edges:6], standard] As you might have noticed from the diagrams of these graphs or from
the output of the Gremlin Console itself, these toy graphs are small (only a few vertices and edges each). It is nice
to have a small graph when learning Gremlin, so that you can easily see if you are getting the results you expect. Even
though these graphs are "small", they are robust enough in structure to try out many different kinds of traversals.
However, if you find that a larger graph might be helpful, there is another option: The Grateful Dead
(schema).
As you might have noticed from the diagrams of these graphs or from
the output of the Gremlin Console itself, these toy graphs are small (only a few vertices and edges each). It is nice
to have a small graph when learning Gremlin, so that you can easily see if you are getting the results you expect. Even
though these graphs are "small", they are robust enough in structure to try out many different kinds of traversals.
However, if you find that a larger graph might be helpful, there is another option: The Grateful Dead
(schema).
gremlin> graph = TinkerGraph.open()
==>tinkergraph[vertices:0 edges:0]
gremlin> graph.io(gryo()).readGraph('data/grateful-dead.kryo')
==>null
gremlin> graph
==>tinkergraph[vertices:808 edges:8049]The Grateful Dead graph ships with the Gremlin Console and the data can be found in several formats (along with the
other toy graphs previously mentioned) in the console’s data directory.
|
Tip
|
If you find yourself in a position where you need to ask a question on the Gremlin Users mailing list about a traversal that you are having trouble with in your application, try to convert the gist of it to one of the toy graphs. Taking this step will make it easier for advanced Gremlin users to help you, which should lead to a faster response time for your problem. In addition, there is the added benefit that the mailing list post will be more relevant to other users, as it is not written solely in the context of your domain. |
As you get familiar with the console, it is good to know what some of the basic commands are. A "command" is not
"Gremlin code", but something interpreted by the console to have special meaning in terms of configuring how the
console works or performing a particular function outside of code itself. These commands are itemized in the
reference documentation, but they can also
be accessed within the console itself with the :help command.
gremlin> :help
For information about Groovy, visit:
http://groovy-lang.org
Available commands:
:help (:h ) Display this help message
? (:? ) Alias to: :help
:exit (:x ) Exit the shell
:quit (:q ) Alias to: :exit
import (:i ) Import a class into the namespace
:display (:d ) Display the current buffer
:clear (:c ) Clear the buffer and reset the prompt counter
:show (:S ) Show variables, classes or imports
:inspect (:n ) Inspect a variable or the last result with the GUI object browser
:purge (:p ) Purge variables, classes, imports or preferences
:edit (:e ) Edit the current buffer
:load (:l ) Load a file or URL into the buffer
. (:. ) Alias to: :load
:save (:s ) Save the current buffer to a file
:record (:r ) Record the current session to a file
:history (:H ) Display, manage and recall edit-line history
:alias (:a ) Create an alias
:register (:rc ) Register a new command with the shell
:doc (:D ) Open a browser window displaying the doc for the argument
:set (:= ) Set (or list) preferences
:uninstall (:- ) Uninstall a Maven library and its dependencies from the Gremlin Console
:install (:+ ) Install a Maven library and its dependencies into the Gremlin Console
:plugin (:pin) Manage plugins for the Console
:remote (:rem) Define a remote connection
:submit (:> ) Send a Gremlin script to Gremlin Server
For help on a specific command type:
:help command
The :help command shows a list of all the commands registered to the console and as this console is based on the
Groovy Shell, you will see commands that are inherited from there in
addition to the ones provided by TinkerPop. You can also request help on a specific command:
gremlin> :help :remote
usage: :remote [current|connect <type-of-remote> [<args>]|config <args>|list|next|prev|choose <index>|close]
Define and manage remote connections to use in conjunction with the :submit command, which will send Gremlin scripts to the specified remote agent for processing.
The Gremlin Console can also provide you with code help via auto-complete functionality. Use the <TAB> key to
trigger a search of possible method names that might complete what you’ve typed to that point.
As you learn more about Gremlin, you will find many code examples in the documentation and most all will be executable in the console. Trying these examples for yourself and modifying their execution slightly to see how output changes is a good way to go about your Gremlin education.
Use Case: Application Development
 You are an application developer and the TinkerPop stack
will be central to your application architecture. You need to develop a series of services that will execute queries
against a graph database in support of the application front-end.
You are an application developer and the TinkerPop stack
will be central to your application architecture. You need to develop a series of services that will execute queries
against a graph database in support of the application front-end.
Most application developers use an IDE, such as Intellij, to help with their software development efforts. The IDE provides shortcuts and conveniences that make complex engineering jobs more productive. When developing applications for TinkerPop, the Gremlin Console should accompany the IDE as an additional tool to enhance that productivity. In other words, when you open your IDE, open the Gremlin Console next to it.
You will find that as you write Gremlin for your code base in your IDE, you will inevitably reach a point of sufficient complexity in your traversals where you will need to:
-
Quickly test the traversal over real data to determine if it is correct.
-
Test or debug pieces of the traversal in isolation.
-
Experiment with different ways of expressing the same traversal.
-
Examine the performance of a traversal through profile() step or by other profiling and benchmarking methods.
Consider an example where you are developing an application that uses TinkerGraph and the data from the "modern" toy graph. You want to encapsulate some logic for a graph traversal that finds a "person" vertex, iterates outgoing edges and groups the adjacent vertices as "value maps".
As you have read the TinkerPop documentation and have been experimenting with Gremlin for a while, you head to your IDE with your open project in it and write a simple class like this:
package com.my.company;
import org.apache.tinkerpop.gremlin.structure.Vertex;
import org.apache.tinkerpop.gremlin.process.traversal.dsl.graph.GraphTraversalSource;
import static org.apache.tinkerpop.gremlin.structure.T.*;
import static org.apache.tinkerpop.gremlin.process.traversal.dsl.graph.__.*;
import java.util.List;
import java.util.Map;
public final class Traversals {
public static Map<String,List<Vertex>> groupAround(GraphTraversalSource g, long vertexId) {
return g.V(vertexId).outE().group().by(label).by(inV()).next()
}
}|
Note
|
TinkerPop code samples typically use static importing,
which allows for a more fluid code style. If the static import above were removed in favor of a standard import of
the __ and T classes, the traversal would read as follows: g.V(id).outE().group().by(T.label).by(__.inV()).next().
The console automatically performs the static imports for these methods, so they do not need to be imported again
in that environment.
|
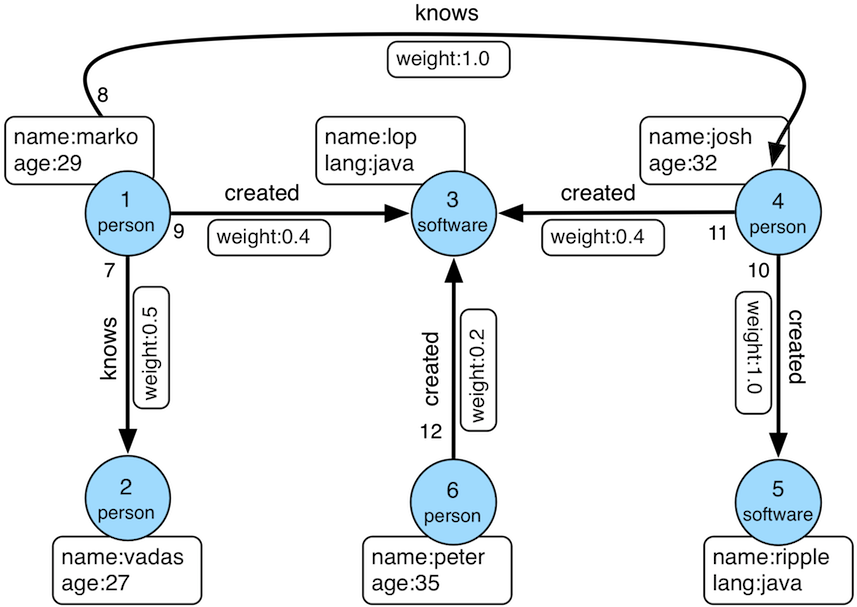
The diagram above displays the "modern" graph for reference. Assuming that g refers to a TraversalSource generated
from a Graph instance that refers to that graph, calling groupAround with "1" as the vertexId argument, should
return a Map with two keys: "knows" and "created", where the "knows" key should have vertices "2" and "4" and the
"created" key should have vertex "3". As you are a good developer, you know to write a unit test to validate this
outcome. You write your test, compile your application, and execute your test only to find it failing on the "knows"
key, which only has one vertex associated to it instead of two.
As you have the Gremlin Console open you decide to debug the problem there. You copy your Gremlin code from the IDE and execute it in the console and confirm the failure:
gremlin> g.V(1).outE().group().by(label).by(inV())
==>[created:v[3], knows:v[2]]Note that next() is removed here. The Gremlin Console automatically tries to iterate all results from a line of
execution. In the above case, that line returns a Traversal. A Traversal is an Iterator and when the console
detects that type it steps through each item in the Iterator and prints it to the screen.
Trying it with the use of next() produces the following:
gremlin> g.V(1).outE().group().by(label).by(inV()).next()
==>created=v[3]
==>knows=v[2]In this case, the line of execution does not return a Traversal. It returns the first item in the Traversal with
the call to next(). This first item is a Map. When the console detects that it is a Map, it iterates the
entrySet() and prints each Map.Entry to the screen. It is possible to "prevent" auto-iteration, which is useful
when you want to work with a Traversal as a variable. You can do this with a clever use of a semi-colon:
gremlin> t = g.V(1).outE().group().by(label).by(inV());null
==>null
gremlin> t.next()
==>created=v[3]
==>knows=v[2]|
Tip
|
In addition to "returning null", you could also return an empty list as in: ‘t = g.V(1);[]’. |
 The first line assigns the
The first line assigns the Traversal to t, but the line itself
is actually two lines of code as denoted by the semi-colon. The line of execution actually returns null, which is
what the console actual auto-iterates. At that point you can work with t as you desire.
Turning your attention back to the original problem, you can now think about the issue with the Traversal not
containing the appropriate number of vertices in the context of iteration. In the original Traversal the second
by() modulator takes inV() as an argument (an anonymous Traversal spawned from the __ class whose methods are
statically imported to the console). This by() tells Gremlin what aspect of the current group of edges should be
stored in the list associated with that group. By specifying inV() you are saying that you want to store the
in-vertices of the
edges for a group.
|
Warning
|
While convenient, statically imported methods can be confusing for new users, especially those who are
translating their code between the console (which is Groovy-based) and a Java IDE. Take care with the use of the
in() method in this context, as the word in is reserved in Groovy. For the console, you must explicitly use
this method as __.in().
|
Structurally, this Traversal is sound, however it makes an assumption about how inV() will be utilized as an inner
Traversal. It is always important to remember that the console does not auto-iterate every Traversal in your
script. It only iterates the result of a line of execution. Therefore, inner Traversal instances do not get that
benefit, and as such, inV() only has next() called upon it pulling a single vertex from the "knows" edges. You
can remedy that by adding fold() to inV() as follows:
gremlin> g.V(1).outE().group().by(label).by(inV().fold()).next()
==>created=[v[3]]
==>knows=[v[2], v[4]]You can now see that your result is as expected and can modify your Java class to reflect the change:
package com.my.company;
import org.apache.tinkerpop.gremlin.structure.Vertex;
import org.apache.tinkerpop.gremlin.process.traversal.dsl.graph.GraphTraversalSource;
import static org.apache.tinkerpop.gremlin.structure.T.*;
import static org.apache.tinkerpop.gremlin.process.traversal.dsl.graph.__.*;
import java.util.List;
import java.util.Map;
public final class Traversals {
public static Map<String,List<Vertex>> groupAround(GraphTraversalSource g, long vertexId) {
return g.V(vertexId).outE().group().by(label).by(inV().fold()).next()
}
}Result iteration represents the most common "simple" bug that users encounter. It’s all too easy to write a traversal as follows:
gremlin> g.V().has('name','marko').drop()
gremlin> g.V().has('name','marko').count()
==>0As you can see, the first traversal removes vertices with the "name" field of "marko" and the second traversal verifies that there are no vertices named "marko" after the first is executed. After seeing success like that in the console, it is all too tempting to copy and paste that line of code to a Java class like:
package com.my.company;
import org.apache.tinkerpop.gremlin.process.traversal.dsl.graph.GraphTraversalSource;
public final class Traversals {
public static void removeByName(GraphTraversalSource g, String name) {
g.V().has("name", name).drop();
}
}Of course, this won’t work and you will likely be left wondering why your unit test for "removeByName" is failing, but
the identical line of code in the console is doing what is expected. The drop() step is not some special form
of terminating step that iterates the traversal - it is just one more step that vertices will pass through. Outside
of the console you must add iterate() as follows:
package com.my.company;
import org.apache.tinkerpop.gremlin.process.traversal.dsl.graph.GraphTraversalSource;
public final class Traversals {
public static void removeByName(GraphTraversalSource g, String name) {
g.V().has("name", name).drop().iterate();
}
}The call to iterate() will do what the console does automatically, executing the Traversal instance and stepping
through the results. You will generally use iterate() to generate side-effects (e.g. drop vertices from the
database), though it has its usage in the console as well. If you have an especially long result set for which
side-effects will be generated, you can simply call iterate() on the traversal and avoid a long stream of output to
the console.
Gremlin written in the console usually has a copy and paste translation to source files (and vice versa). You need
only recall the rules of iteration when you move code between them. It is equally important that you keep an eye on
Traversal objects declared as inner traversals or within lambda expressions where they will not receive automatic
iteration. Keeping these semantics in mind will save you from many annoying debugging sessions.
Use Case: Ad-hoc Analysis
You are doing some general analysis on a graph with Gremlin and decide that you’d like to store those results in Apache Cassandra for additional analysis with other tools.
 The Gremlin Console is an indispensable tool for working
with graph data, but it is also well suited for working with other types of data as well. Its ability to process data
from different sources and formats provides a flexible environment for exploratory analysis. This ability stems from
the underlying Groovy Shell and the fact that any JVM-based libraries are easily imported into it, making their
classes and functions available at the prompt in conjunction with Gremlin.
The Gremlin Console is an indispensable tool for working
with graph data, but it is also well suited for working with other types of data as well. Its ability to process data
from different sources and formats provides a flexible environment for exploratory analysis. This ability stems from
the underlying Groovy Shell and the fact that any JVM-based libraries are easily imported into it, making their
classes and functions available at the prompt in conjunction with Gremlin.
Let’s consider an example where you are exploring "The Crew" toy graph and that you are interested in doing some analysis on where people live and when they lived there. You decide to start simple and just get a basic feeling for the data of the "person" vertices in the graph:
gremlin> graph = TinkerFactory.createTheCrew()
==>tinkergraph[vertices:6 edges:14]
gremlin> g = graph.traversal()
==>graphtraversalsource[tinkergraph[vertices:6 edges:14], standard]
gremlin>
gremlin> g.V().hasLabel('person').valueMap()
==>[name:[marko], location:[san diego, santa cruz, brussels, santa fe]]
==>[name:[stephen], location:[centreville, dulles, purcellville]]
==>[name:[matthias], location:[bremen, baltimore, oakland, seattle]]
==>[name:[daniel], location:[spremberg, kaiserslautern, aachen]]You can see from the output above that there are four "person" vertices and each has a "name" property and a "location" property. The "location" is actually a multi-property, where "location" does not have one value, but several. If you look a bit closer you can also see that each "location" has meta-properties as well:
gremlin> g.V().hasLabel('person').as('person').
properties('location').as('location').
select('person','location').by('name').by(valueMap())
==>[person:marko, location:[startTime:1997, endTime:2001]]
==>[person:marko, location:[startTime:2001, endTime:2004]]
==>[person:marko, location:[startTime:2004, endTime:2005]]
==>[person:marko, location:[startTime:2005]]
==>[person:stephen, location:[startTime:1990, endTime:2000]]
==>[person:stephen, location:[startTime:2000, endTime:2006]]
==>[person:stephen, location:[startTime:2006]]
==>[person:matthias, location:[startTime:2004, endTime:2007]]
==>[person:matthias, location:[startTime:2007, endTime:2011]]
==>[person:matthias, location:[startTime:2011, endTime:2014]]
==>[person:matthias, location:[startTime:2014]]
==>[person:daniel, location:[startTime:1982, endTime:2005]]
==>[person:daniel, location:[startTime:2005, endTime:2009]]
==>[person:daniel, location:[startTime:2009]]You are pleased. You like that you have the basic data present to achieve your goal, but you see a couple of problems. First, given a quick glance at the data, you can see that the data doesn’t uniformly start at a particular time. You were hoping to see data presented in such a way that each "person" had data starting and ending in the same years. The second problem you can see is that the data really isn’t in a format that you need. Ideally, you would like to have something that had rows and columns that was easily dumped to CSV for use in other tools. You currently have the data in two separate traversals and the data is nested.

As a first step to solving your problems, you first need to determine the earliest "startTime" that is common to all the "person" vertices, as this will be the main filter for the data you intend to retrieve:
gremlin> firstYear = g.V().hasLabel('person').
local(properties('location').values('startTime').min()).
max().next()
==>2004You store that result in a variable called "firstYear", as you will likely need that later to help filter results in the traversal that ultimately gets the data. It is often helpful to store results from traversals if you intend to work with that data later and the traversal itself is expensive to execute. It is only important to keep in mind that you will be limited by the memory available to the console.
|
Tip
|
You can change the amount of memory allotted to the console by altering its -Xmx setting in bin/gremlin.sh.
This setting controls the maximum size of the JVM memory allocation pool. To set this value to 1024 megabytes, you
would set this value as follows: -Xmx1024m. It is likely best to append this setting to the initialization of the
JAVA_OPTIONS variable in that script. If you choose to override JAVA_OPTIONS, be sure to examine the default
settings in bin/gremlin.sh to include them as they should not be omitted in your override.
|
In an attempt to test things out, you take a naive approach at the traversal with your filter for "firstYear" applied:
gremlin> firstYear = g.V().hasLabel('person').
local(properties('location').values('startTime').min()).
max().next()
==>2004
gremlin> l = g.V().hasLabel('person').as('person').
properties('location').or(has('endTime',gt(firstYear)),hasNot('endTime')).as('location').
valueMap().as('times').
select('person','location','times').by('name').by(value).by().toList()
==>[person:marko, location:brussels, times:[startTime:2004, endTime:2005]]
==>[person:marko, location:santa fe, times:[startTime:2005]]
==>[person:stephen, location:dulles, times:[startTime:2000, endTime:2006]]
==>[person:stephen, location:purcellville, times:[startTime:2006]]
==>[person:matthias, location:bremen, times:[startTime:2004, endTime:2007]]
==>[person:matthias, location:baltimore, times:[startTime:2007, endTime:2011]]
==>[person:matthias, location:oakland, times:[startTime:2011, endTime:2014]]
==>[person:matthias, location:seattle, times:[startTime:2014]]
==>[person:daniel, location:spremberg, times:[startTime:1982, endTime:2005]]
==>[person:daniel, location:kaiserslautern, times:[startTime:2005, endTime:2009]]
==>[person:daniel, location:aachen, times:[startTime:2009]]As you scan through the data, you can see that it appears to cover the range of time you were looking for. Of course, you still have the problem of the format of the data. Recalling that the Gremlin Console is an extension of the Groovy Console, you decide to just process "l" with some Groovy syntax to coerce it into the format that you would like to see for your rows and columns style output:
gremlin> firstYear = g.V().hasLabel('person').
local(properties('location').values('startTime').min()).
max().next()
==>2004
gremlin> l = g.V().hasLabel('person').as('person').
properties('location').or(has('endTime',gt(firstYear)),hasNot('endTime')).as('location').
valueMap().as('times').
select('person','location','times').by('name').by(value).by().toList()
==>[person:marko, location:brussels, times:[startTime:2004, endTime:2005]]
==>[person:marko, location:santa fe, times:[startTime:2005]]
==>[person:stephen, location:dulles, times:[startTime:2000, endTime:2006]]
==>[person:stephen, location:purcellville, times:[startTime:2006]]
==>[person:matthias, location:bremen, times:[startTime:2004, endTime:2007]]
==>[person:matthias, location:baltimore, times:[startTime:2007, endTime:2011]]
==>[person:matthias, location:oakland, times:[startTime:2011, endTime:2014]]
==>[person:matthias, location:seattle, times:[startTime:2014]]
==>[person:daniel, location:spremberg, times:[startTime:1982, endTime:2005]]
==>[person:daniel, location:kaiserslautern, times:[startTime:2005, endTime:2009]]
==>[person:daniel, location:aachen, times:[startTime:2009]]
gremlin> l.collect{
row->((Math.max(row.times.startTime,firstYear))..((row.times.endTime?:2017)-1)).collect{
year->[person:row.person,location:row.location,year:year]}}.flatten()
==>[person:marko, location:brussels, year:2004]
==>[person:marko, location:santa fe, year:2005]
==>[person:marko, location:santa fe, year:2006]
==>[person:marko, location:santa fe, year:2007]
==>[person:marko, location:santa fe, year:2008]
==>[person:marko, location:santa fe, year:2009]
==>[person:marko, location:santa fe, year:2010]
==>[person:marko, location:santa fe, year:2011]
==>[person:marko, location:santa fe, year:2012]
==>[person:marko, location:santa fe, year:2013]
==>[person:marko, location:santa fe, year:2014]
==>[person:marko, location:santa fe, year:2015]
==>[person:marko, location:santa fe, year:2016]
==>[person:stephen, location:dulles, year:2004]
==>[person:stephen, location:dulles, year:2005]
==>[person:stephen, location:purcellville, year:2006]
==>[person:stephen, location:purcellville, year:2007]
==>[person:stephen, location:purcellville, year:2008]
==>[person:stephen, location:purcellville, year:2009]
==>[person:stephen, location:purcellville, year:2010]
==>[person:stephen, location:purcellville, year:2011]
==>[person:stephen, location:purcellville, year:2012]
==>[person:stephen, location:purcellville, year:2013]
==>[person:stephen, location:purcellville, year:2014]
==>[person:stephen, location:purcellville, year:2015]
==>[person:stephen, location:purcellville, year:2016]
==>[person:matthias, location:bremen, year:2004]
==>[person:matthias, location:bremen, year:2005]
==>[person:matthias, location:bremen, year:2006]
==>[person:matthias, location:baltimore, year:2007]
==>[person:matthias, location:baltimore, year:2008]
==>[person:matthias, location:baltimore, year:2009]
==>[person:matthias, location:baltimore, year:2010]
==>[person:matthias, location:oakland, year:2011]
==>[person:matthias, location:oakland, year:2012]
==>[person:matthias, location:oakland, year:2013]
==>[person:matthias, location:seattle, year:2014]
==>[person:matthias, location:seattle, year:2015]
==>[person:matthias, location:seattle, year:2016]
==>[person:daniel, location:spremberg, year:2004]
==>[person:daniel, location:kaiserslautern, year:2005]
==>[person:daniel, location:kaiserslautern, year:2006]
==>[person:daniel, location:kaiserslautern, year:2007]
==>[person:daniel, location:kaiserslautern, year:2008]
==>[person:daniel, location:aachen, year:2009]
==>[person:daniel, location:aachen, year:2010]
==>[person:daniel, location:aachen, year:2011]
==>[person:daniel, location:aachen, year:2012]
==>[person:daniel, location:aachen, year:2013]
==>[person:daniel, location:aachen, year:2014]
==>[person:daniel, location:aachen, year:2015]
==>[person:daniel, location:aachen, year:2016]You had to apply a bit of brute force, but now you have the rows and columns you wanted, with the data normalized and flattened in such a way that each year since "2004" is represented all the way up to "2016".
 Unfortunately, you are unsatisfied. The added Groovy processing of
"l" feels "wrong" despite it producing the correct output. It has that unfortunate hack for dealing with the
possibility that the "endTime" property contains a "null" value, thus hard-coding the "2017" year into the it (you
want the years through "2016"). You also recall that the Gremlin language has advanced considerably in TinkerPop 3.x
and that it is usually possible to eliminate closures and other direct processing with Groovy. With those issues in
mind, you look to enhance your work.
Unfortunately, you are unsatisfied. The added Groovy processing of
"l" feels "wrong" despite it producing the correct output. It has that unfortunate hack for dealing with the
possibility that the "endTime" property contains a "null" value, thus hard-coding the "2017" year into the it (you
want the years through "2016"). You also recall that the Gremlin language has advanced considerably in TinkerPop 3.x
and that it is usually possible to eliminate closures and other direct processing with Groovy. With those issues in
mind, you look to enhance your work.
A first step would be to get rid of the hard-coded "2017". You decide to get the current year programmatically by
using java.time.Year. This class is not one that is available by default in the console. You might think of this as
similar to what happens when you decide to use a particular class in a Java file. You must "import" the classes that
you wish to use. To do this, you need to use the import command:
gremlin> import java.time.Year
==>groovy.grape.Grape, org.apache.commons.configuration.*, org.apache.tinkerpop.gremlin.process.traversal.strategy.verification.*, org.apache.tinkerpop.gremlin.process.computer.bulkloading.*, org.apache.tinkerpop.gremlin.process.computer.traversal.*, org.apache.tinkerpop.gremlin.util.function.*, org.apache.tinkerpop.gremlin.structure.io.*, org.apache.tinkerpop.gremlin.process.computer.ranking.pagerank.*, groovy.sql.*, org.apache.tinkerpop.gremlin.groovy.loaders.*, groovy.json.*, org.apache.tinkerpop.gremlin.process.traversal.dsl.graph.*, org.apache.tinkerpop.gremlin.structure.*, org.apache.tinkerpop.gremlin.process.traversal.strategy.decoration.*, org.apache.tinkerpop.gremlin.process.traversal.engine.*, org.apache.tinkerpop.gremlin.structure.io.gryo.*, org.apache.tinkerpop.gremlin.process.traversal.strategy.optimization.*, org.apache.tinkerpop.gremlin.process.traversal.step.util.event.*, org.apache.tinkerpop.gremlin.util.*, org.apache.tinkerpop.gremlin.structure.util.*, org.apache.tinkerpop.gremlin.structure.io.graphml.*, org.apache.tinkerpop.gremlin.process.computer.*, org.apache.tinkerpop.gremlin.process.traversal.strategy.finalization.*, org.apache.tinkerpop.gremlin.process.computer.clustering.peerpressure.*, org.apache.tinkerpop.gremlin.structure.util.detached.*, org.apache.tinkerpop.gremlin.structure.io.graphson.*, org.apache.tinkerpop.gremlin.process.traversal.*, org.apache.tinkerpop.gremlin.process.computer.bulkdumping.*, org.apache.tinkerpop.gremlin.process.traversal.util.*, org.apache.tinkerpop.gremlin.groovy.function.*, static org.apache.tinkerpop.gremlin.process.traversal.SackFunctions.Barrier.*, static org.apache.tinkerpop.gremlin.util.TimeUtil.*, static org.apache.tinkerpop.gremlin.structure.Direction.*, static org.apache.tinkerpop.gremlin.process.traversal.Pop.*, static org.apache.tinkerpop.gremlin.process.traversal.step.TraversalOptionParent.Pick.*, static org.apache.tinkerpop.gremlin.structure.VertexProperty.Cardinality.*, static org.apache.tinkerpop.gremlin.process.traversal.dsl.graph.GraphTraversalSource.*, static org.apache.tinkerpop.gremlin.process.traversal.P.*, static org.apache.tinkerpop.gremlin.process.traversal.Order.*, static org.apache.tinkerpop.gremlin.process.traversal.dsl.graph.__.*, static org.apache.tinkerpop.gremlin.structure.io.IoCore.*, static org.apache.tinkerpop.gremlin.process.traversal.Scope.*, static org.apache.tinkerpop.gremlin.structure.Column.*, static org.apache.tinkerpop.gremlin.structure.T.*, static org.apache.tinkerpop.gremlin.process.traversal.Operator.*, org.apache.tinkerpop.gremlin.driver.ser.*, org.apache.tinkerpop.gremlin.driver.message.*, org.apache.tinkerpop.gremlin.driver.exception.*, org.apache.tinkerpop.gremlin.driver.*, static groovyx.gbench.BenchmarkStaticExtension.*, static groovyx.gprof.ProfileStaticExtension.*, groovyx.gprof.*, groovyx.gbench.*, org.apache.tinkerpop.gremlin.giraph.process.computer.*, org.apache.tinkerpop.gremlin.groovy.plugin.dsl.credential.CredentialGraph, static org.apache.tinkerpop.gremlin.groovy.plugin.dsl.credential.CredentialGraph.*, org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.lib.input.SequenceFileInputFormat, org.apache.hadoop.hdfs.*, org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.lib.input.*, org.apache.tinkerpop.gremlin.hadoop.structure.io.*, org.apache.tinkerpop.gremlin.hadoop.process.computer.mapreduce.*, org.apache.hadoop.conf.*, org.apache.hadoop.util.*, org.apache.tinkerpop.gremlin.hadoop.structure.io.gryo.*, org.apache.tinkerpop.gremlin.hadoop.structure.*, org.apache.hadoop.io.compress.*, org.apache.tinkerpop.gremlin.hadoop.*, org.apache.tinkerpop.gremlin.hadoop.structure.io.graphson.*, org.apache.hadoop.io.*, org.apache.log4j.*, org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.lib.output.*, org.apache.tinkerpop.gremlin.hadoop.structure.io.script.*, org.apache.tinkerpop.gremlin.hadoop.structure.util.*, org.apache.hadoop.fs.*, org.apache.tinkerpop.gremlin.neo4j.structure.*, static org.apache.tinkerpop.gremlin.neo4j.process.traversal.LabelP.*, org.apache.tinkerpop.gremlin.spark.process.computer.*, org.apache.tinkerpop.gremlin.spark.structure.*, org.apache.tinkerpop.gremlin.spark.structure.io.*, org.apache.tinkerpop.gremlin.tinkergraph.structure.*, org.apache.tinkerpop.gremlin.tinkergraph.process.computer.*, java.time.Year
gremlin> Year.now()
==>2017You can now use Year with the constant() step,
to produce the set of years to have for each person up to the current year:
gremlin> import java.time.Year
==>groovy.grape.Grape, org.apache.commons.configuration.*, org.apache.tinkerpop.gremlin.process.traversal.strategy.verification.*, org.apache.tinkerpop.gremlin.process.computer.bulkloading.*, org.apache.tinkerpop.gremlin.process.computer.traversal.*, org.apache.tinkerpop.gremlin.util.function.*, org.apache.tinkerpop.gremlin.structure.io.*, org.apache.tinkerpop.gremlin.process.computer.ranking.pagerank.*, groovy.sql.*, org.apache.tinkerpop.gremlin.groovy.loaders.*, groovy.json.*, org.apache.tinkerpop.gremlin.process.traversal.dsl.graph.*, org.apache.tinkerpop.gremlin.structure.*, org.apache.tinkerpop.gremlin.process.traversal.strategy.decoration.*, org.apache.tinkerpop.gremlin.process.traversal.engine.*, org.apache.tinkerpop.gremlin.structure.io.gryo.*, org.apache.tinkerpop.gremlin.process.traversal.strategy.optimization.*, org.apache.tinkerpop.gremlin.process.traversal.step.util.event.*, org.apache.tinkerpop.gremlin.util.*, org.apache.tinkerpop.gremlin.structure.util.*, org.apache.tinkerpop.gremlin.structure.io.graphml.*, org.apache.tinkerpop.gremlin.process.computer.*, org.apache.tinkerpop.gremlin.process.traversal.strategy.finalization.*, org.apache.tinkerpop.gremlin.process.computer.clustering.peerpressure.*, org.apache.tinkerpop.gremlin.structure.util.detached.*, org.apache.tinkerpop.gremlin.structure.io.graphson.*, org.apache.tinkerpop.gremlin.process.traversal.*, org.apache.tinkerpop.gremlin.process.computer.bulkdumping.*, org.apache.tinkerpop.gremlin.process.traversal.util.*, org.apache.tinkerpop.gremlin.groovy.function.*, static org.apache.tinkerpop.gremlin.process.traversal.SackFunctions.Barrier.*, static org.apache.tinkerpop.gremlin.util.TimeUtil.*, static org.apache.tinkerpop.gremlin.structure.Direction.*, static org.apache.tinkerpop.gremlin.process.traversal.Pop.*, static org.apache.tinkerpop.gremlin.process.traversal.step.TraversalOptionParent.Pick.*, static org.apache.tinkerpop.gremlin.structure.VertexProperty.Cardinality.*, static org.apache.tinkerpop.gremlin.process.traversal.dsl.graph.GraphTraversalSource.*, static org.apache.tinkerpop.gremlin.process.traversal.P.*, static org.apache.tinkerpop.gremlin.process.traversal.Order.*, static org.apache.tinkerpop.gremlin.process.traversal.dsl.graph.__.*, static org.apache.tinkerpop.gremlin.structure.io.IoCore.*, static org.apache.tinkerpop.gremlin.process.traversal.Scope.*, static org.apache.tinkerpop.gremlin.structure.Column.*, static org.apache.tinkerpop.gremlin.structure.T.*, static org.apache.tinkerpop.gremlin.process.traversal.Operator.*, org.apache.tinkerpop.gremlin.driver.ser.*, org.apache.tinkerpop.gremlin.driver.message.*, org.apache.tinkerpop.gremlin.driver.exception.*, org.apache.tinkerpop.gremlin.driver.*, static groovyx.gbench.BenchmarkStaticExtension.*, static groovyx.gprof.ProfileStaticExtension.*, groovyx.gprof.*, groovyx.gbench.*, org.apache.tinkerpop.gremlin.giraph.process.computer.*, org.apache.tinkerpop.gremlin.groovy.plugin.dsl.credential.CredentialGraph, static org.apache.tinkerpop.gremlin.groovy.plugin.dsl.credential.CredentialGraph.*, org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.lib.input.SequenceFileInputFormat, org.apache.hadoop.hdfs.*, org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.lib.input.*, org.apache.tinkerpop.gremlin.hadoop.structure.io.*, org.apache.tinkerpop.gremlin.hadoop.process.computer.mapreduce.*, org.apache.hadoop.conf.*, org.apache.hadoop.util.*, org.apache.tinkerpop.gremlin.hadoop.structure.io.gryo.*, org.apache.tinkerpop.gremlin.hadoop.structure.*, org.apache.hadoop.io.compress.*, org.apache.tinkerpop.gremlin.hadoop.*, org.apache.tinkerpop.gremlin.hadoop.structure.io.graphson.*, org.apache.hadoop.io.*, org.apache.log4j.*, org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.lib.output.*, org.apache.tinkerpop.gremlin.hadoop.structure.io.script.*, org.apache.tinkerpop.gremlin.hadoop.structure.util.*, org.apache.hadoop.fs.*, org.apache.tinkerpop.gremlin.neo4j.structure.*, static org.apache.tinkerpop.gremlin.neo4j.process.traversal.LabelP.*, org.apache.tinkerpop.gremlin.spark.process.computer.*, org.apache.tinkerpop.gremlin.spark.structure.*, org.apache.tinkerpop.gremlin.spark.structure.io.*, org.apache.tinkerpop.gremlin.tinkergraph.structure.*, org.apache.tinkerpop.gremlin.tinkergraph.process.computer.*, java.time.Year
gremlin> firstYear = g.V().hasLabel('person').
local(properties('location').values('startTime').min()).
max().next()
==>2004
gremlin> g.V().hasLabel("person").as("person").
constant((firstYear..(Year.now().value)).toList()).unfold().as("year").
select('person','year').by('name').by()
==>[person:marko, year:2004]
==>[person:marko, year:2005]
==>[person:marko, year:2006]
==>[person:marko, year:2007]
==>[person:marko, year:2008]
==>[person:marko, year:2009]
==>[person:marko, year:2010]
==>[person:marko, year:2011]
==>[person:marko, year:2012]
==>[person:marko, year:2013]
==>[person:marko, year:2014]
==>[person:marko, year:2015]
==>[person:marko, year:2016]
==>[person:marko, year:2017]
==>[person:stephen, year:2004]
==>[person:stephen, year:2005]
==>[person:stephen, year:2006]
==>[person:stephen, year:2007]
==>[person:stephen, year:2008]
==>[person:stephen, year:2009]
==>[person:stephen, year:2010]
==>[person:stephen, year:2011]
==>[person:stephen, year:2012]
==>[person:stephen, year:2013]
==>[person:stephen, year:2014]
==>[person:stephen, year:2015]
==>[person:stephen, year:2016]
==>[person:stephen, year:2017]
==>[person:matthias, year:2004]
==>[person:matthias, year:2005]
==>[person:matthias, year:2006]
==>[person:matthias, year:2007]
==>[person:matthias, year:2008]
==>[person:matthias, year:2009]
==>[person:matthias, year:2010]
==>[person:matthias, year:2011]
==>[person:matthias, year:2012]
==>[person:matthias, year:2013]
==>[person:matthias, year:2014]
==>[person:matthias, year:2015]
==>[person:matthias, year:2016]
==>[person:matthias, year:2017]
==>[person:daniel, year:2004]
==>[person:daniel, year:2005]
==>[person:daniel, year:2006]
==>[person:daniel, year:2007]
==>[person:daniel, year:2008]
==>[person:daniel, year:2009]
==>[person:daniel, year:2010]
==>[person:daniel, year:2011]
==>[person:daniel, year:2012]
==>[person:daniel, year:2013]
==>[person:daniel, year:2014]
==>[person:daniel, year:2015]
==>[person:daniel, year:2016]
==>[person:daniel, year:2017]From there you can build on that traversal to grab the "location" given the generated "year" for that data:
gremlin> import java.time.Year
==>groovy.grape.Grape, org.apache.commons.configuration.*, org.apache.tinkerpop.gremlin.process.traversal.strategy.verification.*, org.apache.tinkerpop.gremlin.process.computer.bulkloading.*, org.apache.tinkerpop.gremlin.process.computer.traversal.*, org.apache.tinkerpop.gremlin.util.function.*, org.apache.tinkerpop.gremlin.structure.io.*, org.apache.tinkerpop.gremlin.process.computer.ranking.pagerank.*, groovy.sql.*, org.apache.tinkerpop.gremlin.groovy.loaders.*, groovy.json.*, org.apache.tinkerpop.gremlin.process.traversal.dsl.graph.*, org.apache.tinkerpop.gremlin.structure.*, org.apache.tinkerpop.gremlin.process.traversal.strategy.decoration.*, org.apache.tinkerpop.gremlin.process.traversal.engine.*, org.apache.tinkerpop.gremlin.structure.io.gryo.*, org.apache.tinkerpop.gremlin.process.traversal.strategy.optimization.*, org.apache.tinkerpop.gremlin.process.traversal.step.util.event.*, org.apache.tinkerpop.gremlin.util.*, org.apache.tinkerpop.gremlin.structure.util.*, org.apache.tinkerpop.gremlin.structure.io.graphml.*, org.apache.tinkerpop.gremlin.process.computer.*, org.apache.tinkerpop.gremlin.process.traversal.strategy.finalization.*, org.apache.tinkerpop.gremlin.process.computer.clustering.peerpressure.*, org.apache.tinkerpop.gremlin.structure.util.detached.*, org.apache.tinkerpop.gremlin.structure.io.graphson.*, org.apache.tinkerpop.gremlin.process.traversal.*, org.apache.tinkerpop.gremlin.process.computer.bulkdumping.*, org.apache.tinkerpop.gremlin.process.traversal.util.*, org.apache.tinkerpop.gremlin.groovy.function.*, static org.apache.tinkerpop.gremlin.process.traversal.SackFunctions.Barrier.*, static org.apache.tinkerpop.gremlin.util.TimeUtil.*, static org.apache.tinkerpop.gremlin.structure.Direction.*, static org.apache.tinkerpop.gremlin.process.traversal.Pop.*, static org.apache.tinkerpop.gremlin.process.traversal.step.TraversalOptionParent.Pick.*, static org.apache.tinkerpop.gremlin.structure.VertexProperty.Cardinality.*, static org.apache.tinkerpop.gremlin.process.traversal.dsl.graph.GraphTraversalSource.*, static org.apache.tinkerpop.gremlin.process.traversal.P.*, static org.apache.tinkerpop.gremlin.process.traversal.Order.*, static org.apache.tinkerpop.gremlin.process.traversal.dsl.graph.__.*, static org.apache.tinkerpop.gremlin.structure.io.IoCore.*, static org.apache.tinkerpop.gremlin.process.traversal.Scope.*, static org.apache.tinkerpop.gremlin.structure.Column.*, static org.apache.tinkerpop.gremlin.structure.T.*, static org.apache.tinkerpop.gremlin.process.traversal.Operator.*, org.apache.tinkerpop.gremlin.driver.ser.*, org.apache.tinkerpop.gremlin.driver.message.*, org.apache.tinkerpop.gremlin.driver.exception.*, org.apache.tinkerpop.gremlin.driver.*, static groovyx.gbench.BenchmarkStaticExtension.*, static groovyx.gprof.ProfileStaticExtension.*, groovyx.gprof.*, groovyx.gbench.*, org.apache.tinkerpop.gremlin.giraph.process.computer.*, org.apache.tinkerpop.gremlin.groovy.plugin.dsl.credential.CredentialGraph, static org.apache.tinkerpop.gremlin.groovy.plugin.dsl.credential.CredentialGraph.*, org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.lib.input.SequenceFileInputFormat, org.apache.hadoop.hdfs.*, org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.lib.input.*, org.apache.tinkerpop.gremlin.hadoop.structure.io.*, org.apache.tinkerpop.gremlin.hadoop.process.computer.mapreduce.*, org.apache.hadoop.conf.*, org.apache.hadoop.util.*, org.apache.tinkerpop.gremlin.hadoop.structure.io.gryo.*, org.apache.tinkerpop.gremlin.hadoop.structure.*, org.apache.hadoop.io.compress.*, org.apache.tinkerpop.gremlin.hadoop.*, org.apache.tinkerpop.gremlin.hadoop.structure.io.graphson.*, org.apache.hadoop.io.*, org.apache.log4j.*, org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.lib.output.*, org.apache.tinkerpop.gremlin.hadoop.structure.io.script.*, org.apache.tinkerpop.gremlin.hadoop.structure.util.*, org.apache.hadoop.fs.*, org.apache.tinkerpop.gremlin.neo4j.structure.*, static org.apache.tinkerpop.gremlin.neo4j.process.traversal.LabelP.*, org.apache.tinkerpop.gremlin.spark.process.computer.*, org.apache.tinkerpop.gremlin.spark.structure.*, org.apache.tinkerpop.gremlin.spark.structure.io.*, org.apache.tinkerpop.gremlin.tinkergraph.structure.*, org.apache.tinkerpop.gremlin.tinkergraph.process.computer.*, java.time.Year
gremlin> firstYear = g.V().hasLabel('person').
local(properties('location').values('startTime').min()).
max().next()
==>2004
gremlin> g.V().hasLabel("person").as("person").
constant((firstYear..(new Date().getYear() + 1900)).toList()).unfold().as("year").
select("person").coalesce(
properties("location").filter(values("startTime").where(gte("year"))).
order().by("startTime").limit(1),
properties("location").hasNot("endTime")).value().as("location").
select("person","year","location").by("name").by().by()
==>[person:marko, year:2004, location:brussels]
==>[person:marko, year:2005, location:santa fe]
==>[person:marko, year:2006, location:santa fe]
==>[person:marko, year:2007, location:santa fe]
==>[person:marko, year:2008, location:santa fe]
==>[person:marko, year:2009, location:santa fe]
==>[person:marko, year:2010, location:santa fe]
==>[person:marko, year:2011, location:santa fe]
==>[person:marko, year:2012, location:santa fe]
==>[person:marko, year:2013, location:santa fe]
==>[person:marko, year:2014, location:santa fe]
==>[person:marko, year:2015, location:santa fe]
==>[person:marko, year:2016, location:santa fe]
==>[person:marko, year:2017, location:santa fe]
==>[person:stephen, year:2004, location:purcellville]
==>[person:stephen, year:2005, location:purcellville]
==>[person:stephen, year:2006, location:purcellville]
==>[person:stephen, year:2007, location:purcellville]
==>[person:stephen, year:2008, location:purcellville]
==>[person:stephen, year:2009, location:purcellville]
==>[person:stephen, year:2010, location:purcellville]
==>[person:stephen, year:2011, location:purcellville]
==>[person:stephen, year:2012, location:purcellville]
==>[person:stephen, year:2013, location:purcellville]
==>[person:stephen, year:2014, location:purcellville]
==>[person:stephen, year:2015, location:purcellville]
==>[person:stephen, year:2016, location:purcellville]
==>[person:stephen, year:2017, location:purcellville]
==>[person:matthias, year:2004, location:bremen]
==>[person:matthias, year:2005, location:baltimore]
==>[person:matthias, year:2006, location:baltimore]
==>[person:matthias, year:2007, location:baltimore]
==>[person:matthias, year:2008, location:oakland]
==>[person:matthias, year:2009, location:oakland]
==>[person:matthias, year:2010, location:oakland]
==>[person:matthias, year:2011, location:oakland]
==>[person:matthias, year:2012, location:seattle]
==>[person:matthias, year:2013, location:seattle]
==>[person:matthias, year:2014, location:seattle]
==>[person:matthias, year:2015, location:seattle]
==>[person:matthias, year:2016, location:seattle]
==>[person:matthias, year:2017, location:seattle]
==>[person:daniel, year:2004, location:kaiserslautern]
==>[person:daniel, year:2005, location:kaiserslautern]
==>[person:daniel, year:2006, location:aachen]
==>[person:daniel, year:2007, location:aachen]
==>[person:daniel, year:2008, location:aachen]
==>[person:daniel, year:2009, location:aachen]
==>[person:daniel, year:2010, location:aachen]
==>[person:daniel, year:2011, location:aachen]
==>[person:daniel, year:2012, location:aachen]
==>[person:daniel, year:2013, location:aachen]
==>[person:daniel, year:2014, location:aachen]
==>[person:daniel, year:2015, location:aachen]
==>[person:daniel, year:2016, location:aachen]
==>[person:daniel, year:2017, location:aachen]|
Tip
|
Not sure what the above traversal is doing? When you come across a traversal that you don’t understand fully, the Gremlin Console is great place to get help. You can dismantle a large traversal and execute it in smaller parts to see what each part produces as output. |
You now have a traversal written with idiomatic Gremlin with the results in the form that you wanted to have. Now you’d like to dump this data to Cassandra for further analysis in another tool. You decide to use the DataStax java-driver in the console to write to Cassandra.

The driver does not come bundled with the console and is not available on its classpath by default. You can bring
other libraries into the console with the :install command. With :install, you can reference the Maven
coordinates (i.e. group, artifact, and version) of a library to have it automatically downloaded from a Maven
repository and placed into the console classpath. If you have read through the reference documentation, you would find
a number of examples of :install usage to bring in unbundled TinkerPop libraries, like
neo4j-gremlin or
hadoop-gremlin.
|
Important
|
Before you use the :install command, please be sure to read the reference documentation on
Grape configuration. If you do not have proper
settings in place, it is likely that the :install command will fail by way of download errors.
|
|
Tip
|
You can also manually "install" dependencies to the console by copying them into the Gremlin Console classpath.
This is most easily accomplished by copying the required jar files to the GREMLIN_HOME/lib directory.
|
gremlin> :install com.datastax.cassandra cassandra-driver-core 2.1.9
==>Loaded: [com.datastax.cassandra, cassandra-driver-core, 2.1.9]
gremlin> import com.datastax.driver.core.*
==>groovy.grape.Grape, org.apache.commons.configuration.*, ..., com.datastax.driver.core.*
gremlin> import static com.datastax.driver.core.querybuilder.QueryBuilder.*
==>groovy.grape.Grape, org.apache.commons.configuration.*, ..., static com.datastax.driver.core.querybuilder.QueryBuilder.*
gremlin> cluster = com.datastax.driver.core.Cluster.builder().addContactPoint("localhost").build()
==>com.datastax.driver.core.Cluster@3e1624c7
gremlin> session = cluster.connect()
==>com.datastax.driver.core.SessionManager@35764bef
gremlin> session.execute("CREATE KEYSPACE crew WITH REPLICATION = { 'class' : 'SimpleStrategy', 'replication_factor' : 3 }")
gremlin> session.execute("USE crew")
gremlin> session.execute("CREATE TABLE locations ( name varchar, location varchar, year int, PRIMARY KEY (name, year))")In the above code, you first use :install to pull in the dependencies of the driver. When that first line has
executed to completion you can inspect the GREMLIN_HOME/ext directory to see that the appropriate jar files have
been copied to the classpath. The remaining lines of code demonstrate how to instantiate a driver instance to
connect to a running Cassandra instance. CQL
statements are then issued to create the keyspace and table to hold the data.
Now that you have a Session established with a table to store the data in, you can iterate through the Traversal
and stream the data to Cassandra:
gremlin> g.V().hasLabel("person").as("person").
gremlin> constant((firstYear..(new Date().getYear() + 1900)).toList()).unfold().as("year").
gremlin> select("person").coalesce(
gremlin> properties("location").filter(values("startTime").where(gte("year"))).
gremlin> order().by("startTime").limit(1),
gremlin> properties("location").hasNot("endTime")).value().as("location").
gremlin> select("person","year","location").by("name").by().by().
gremlin> forEachRemaining{
gremlin> def statement = insertInto("locations").
gremlin> value("name", it.person).
gremlin> value("location", it.location).
gremlin> value("year", it.year)
gremlin> session.execute(statement)
gremlin> }
gremlin> session.execute(select().all().from("locations"))
==>Row[daniel, 2004, kaiserslautern]
==>Row[daniel, 2005, kaiserslautern]
==>Row[daniel, 2006, aachen]
==>Row[daniel, 2007, aachen]
==>Row[daniel, 2008, aachen]
==>Row[daniel, 2009, aachen]
==>Row[daniel, 2010, aachen]
...
==>Row[stephen, 2015, purcellville]
==>Row[stephen, 2016, purcellville]Iteration is performed by the call to forEachRemaining(). The closure supplied to that method is applied to each "row"
in the Traversal. Note the use of def in that closure to declare the "statement" variable. In the console, the
use of def inside a closure scopes that variable to the closure. Without def the "row" variable would
be accessible globally (i.e. at the gremlin> prompt). The use of def at the console prompt for variable definition
is unecessary and will result in error:
gremlin> def x = 10
==>10
gremlin> x
No such property: x for class: groovysh_evaluate
Display stack trace? [yN] n|
Tip
|
If you find that you always work with a particular library, consider starting the console with an initialization
script that prepares your environment for you. An "initialization script" is just a Groovy script that contains the
initial commands to execute when the console starts. Following the use case, it would be nice if the initialization
script contained the import statement for the driver and possibly the code to get the Session object ready for use.
Start the Gremlin Console with that script by just adding it as an argument on the command line:
bin/gremlin.sh init.groovy.
|
This use case focused on using a Cassandra related library, but it should be evident that it would be equally
straightforward to perform this same data dump to HBase,
Microsoft SQL Server,
MongoDB, etc. You should further note, that you are not restricted to a "data dump".
You could just as easily :install libraries to read data from Oracle
into a graph, use functions from Commons Math, or do anything
else you can think of with available JVM libraries.
Summary
These use cases have tried to demonstrate some of the common ways in which you can use the Gremlin Console. In the process, they exposed tips and pitfalls to be aware of when working with it. Hopefully, you have gained some new knowledge on what the console can do for you and have been inspired to work with it in more productive ways.