Ibator Feature Debug Reference
This page contains reference information about how to build and debug the Ibator
feature from source.
Feature Structure
The Ibator feature is structured as five different Eclipse projects - a feature project and
four plugin projects. The feature project groups the four plugins together for easy
installation. The Ibator feature project is org.apache.ibatis.ibator.
This project references the four plugin projects. The plugin projects are structured as
follows:
| Plug-in Project |
Description |
org.apache.ibatis.ibator.core |
This plugin is an Eclipse library plugin for the standard Ibator JAR file.
The purpose of this plug-in is to package the standard JAR and make it available to the
other plugins. There is a build file in this plug-in (buildIbator.xml) that
will compile the core Ibator JAR file and update the wrapped JAR files. This makes
it easy to keep the plugin up to date as the core functionality is developed. |
org.apache.ibatis.ibator.eclipse.core |
This plugin holds Java support classes for the other plugins. This plugin does not contribute
to the Eclipse user interface. Currently, this plugin includes classes for Java file
merging, and Eclipse implementations of the Ibator callback interfaces. |
org.apache.ibatis.ibator.eclipse.doc |
This plug-in holds the documentation for Ibator. There is a build file in this
plug-in (buildDoc.xml) that will build the documentation and package it for inclusion
into the Eclipse help system. |
org.apache.ibatis.ibator.eclipse.ui |
This plug-in holds the Java code for the Eclipse user interface for Ibator. If you
are experiencing trouble with the plugin specific features (like the integrated Ant task), then
the code for those features will be found in this plugin.
|
Building the Feature and Plug-ins from Source
The following instructions show how to build the Ibator feature and plug-ins from the
latest source
in the Subversion repository. We assume that you are somewhat familiar with Subversion
and the Eclipse plug-in development environment (PDE). These instructions also assume
you are using Eclipse version 3.4.1. The plug-in
code is not supported in versions of Eclipse prior to version 3.4.1.
- Checkout the latest source code from Subversion
- Create a local directory where the source will be stored (for example
/Ibator/source)
- Check out the source tree from the Subversion repository at
http://svn.apache.org/repos/asf/ibatis/trunk/java/tools/ibator/
Note: this will also checkout the source for the Ibator core JAR.
- Create a new Eclipse workspace directory (for example /EclipseWorkspaces/Ibator)
- Important: make sure that a version 5.0 or higher JDK is configured as the default
JRE in Eclipse (Window>Preferences>Java>Installed JREs). A JDK is required - a JRE
alone will cause problems.
- Start Eclipse and point it to the new workspace directory
- Import the plug-in projects into the workspace
- Start the Eclipse project import wizard
(File>Import>General>Existing Projects into Workspace)
- Set the root directory to the "eclipse" sub-directory of the directory where
you did the SVN checkout (for example, /Ibator/source/eclipse)
- Select the five projects under the directory, do not copy the projects into
your workspace. The filled out wizard looks like this:
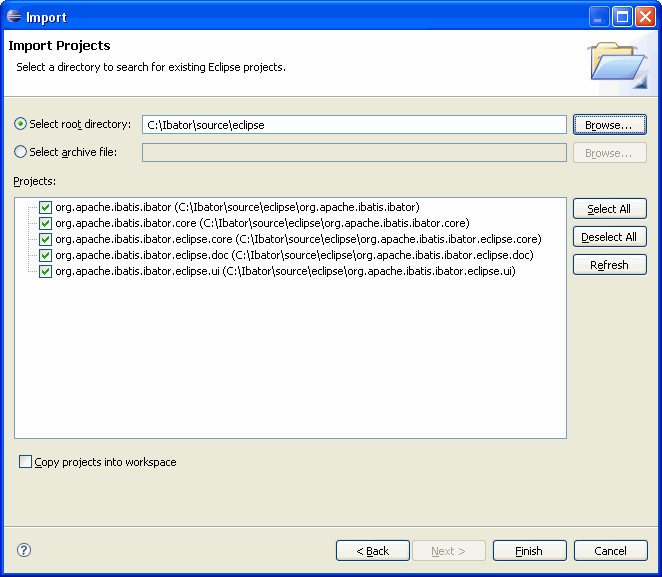
- Press "Finish", wait for the workspace to build.
Debugging
At this point the projects should be successfully compiled in Eclipse. If you want to
debug something in the plug-in, you will need to start another instance of Eclipse
in debug mode. The following instructions explain how to do this.
- Set a breakpoint in the code you would like to debug.
- Double click on the "plugin.xml" file in the "org.apache.ibatis.ibator.eclipse.ui"
project. This should open the plug-in manifest editor. If some other editor
opens, then close the editor, right click on "plugin.xml" and select the
"Open With>Plug-in Manifest Editor" option.
- Select the "Overview" editor tab
- Take the option to "Launch an Eclipse Application in Debug mode". This will
start a new instance of Eclipse in debug mode with the Ibator plug-ins installed.
Once you have the other instance of Eclipse started you should create a new Java project
in the new workspace, create and fill out an Ibator configuration file, and then run Ibator.
Ibator should eventually hit your breakpoint, and then you step through the code.
The following classes will likely be of the most interest in debugging:
| Class |
Description |
org.apache.ibatis.ibator.eclipse.ui.actions.RunIbatorThread |
This class is a thread that runs Ibator on the selected configuration file.
You can set a breakpoint in the run method of this class to follow
the Ibator code generation process from the beginning.
|
org.apache.ibatis.ibator.eclipse.core.merge.JavaFileMerger |
This class implements the Java file merge function. You can set a breakpoint
in the getMergedSource method to follow the merging process.
|
Building the Documentation
The documentation for Ibator is integrated into the Eclipse help system.
The documentation is partially generated (Javadocs), partially copied in from the
core Ibator source tree, and partially maintained in the plugin itself.
This full documentation set is not in Subversion because it is partially generated. If you would
like to rebuild the documentation, simply execute the buildDoc.xml file
in the org.apache.ibatis.ibator.eclipse.doc project (an Ant build file).
Building the Ibator Core JAR in Eclipse
The core Ibator JAR file has it's source code attached in the plugin, so you
should be able to step into core Ibator methods for debug. If you have found a bug
in Ibator, or would like to test an enhancement, you should modify the Ibator source code,
and then rebuild the JAR for inclusion in the plugin.
If you would like to modify/enhance the Ibator core JAR, then you can create a
Java project for the core JAR by following these steps:
- Start the Eclipse new project wizard
(File>New>Project...)
- Select the "Java Project from Existing Ant Buildfile" wizard, press "Next"
- Browse to the "build.xml" file in the checked out project (for example
/Ibator/source/core/build/build.xml). Select the javac task found in target "build.compile".
The other javac tasks are used during the normal Ibator build to compile tests
and test support classes.
Accept the default for the other fields and press "Finish".
- Wait for the workspace to build. Note: you will need to add Ant to the
build path for the project for a successful compile. You can find an Ant JAR
in the ../core/devlib subdirectory of your SVN checkout directory.
Note that Ibator is compiled with JDK 5.0 for distribution.
If you make a change in the Ibator core files, you can use the buildIbator.xml
Ant build file in the org.apache.ibatis.ibator.core project to update the
JAR in the plug-in. Note that this build file does not run the entire Ibator build (i.e. it
does not run the tests).
