The goal of this section is to create a new Java project in Eclipse containing a basic Cayenne mapping. It presents an introduction to CayenneModeler GUI tool, showing how to create the initial mapping objects: DataDomain, DataNode, DataMap.
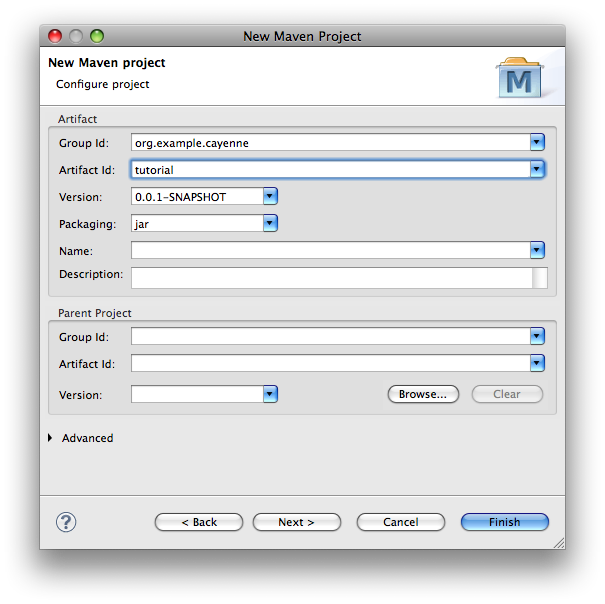
In Eclipse select "File > New > Other..." and then "Maven > Maven Project". Click "Next". On the following screen check "Create a simple project" checkbox and click "Next" again. In the dialog shown on the screenshot below, fill the "Group Id" and "Artifact Id" fields and click "Finish".

Now you should have a new empty project in the Eclipse workspace. Check that the project Java compiler settings are correct. Rightclick on the "tutorial" project, select "Properties > Java Compiler" and ensure that "Compiler compliance level" is at least "1.5" (some versions of Maven plugin seem to be setting it to 1.4 by default).
Although later in this tutorial we'll be using Maven to include Cayenne runtime jars in the project, you'll still need to download Cayenne to get access to the CayenneModeler tool.
| If you are really into Maven, you can start CayenneModeler from Maven if you wish. We'll do it in a more traditional way here. |
Download the latest release from here. Unpack the distribution somewhere in the file system and start CayenneModeler, following platform-specific instructions. On most platforms it is done simply by doubleclicking the Modeler icon. The welcome screen of the Modeler looks like this:

Click on the "New Project" button on Welcome screen. A new mapping project will appear that contains a single DataDomain. The meaning of a DataDomain is explained elsewhere in the User Guide. For now it is sufficient to understand that DataDomain is the root of your mapping project.
The next project object you will create is a DataNode. DataNode is a descriptor of a single database your application will connect to. Cayenne mapping project can use more than one database, but for now, we'll only use one. With "UntitledDomain" selected on the left, click on "Create DataNode" button on the toolbar (or select "Project > Create DataNode" from the menu.
A new DataNode is displayed. Now you need to specify JDBC connection parameters. For an in-memory Derby database you can enter the following settings:
| We are creating an in-memory database here. So when you stop your application, all the data will be lost. In most real-life cases you'll be connecting to a database that actually persists its data on disk, but an in-memory DB will do for the simple tutorial. |
Also you will need to change "Schema Update Strategy". Select "org.apache.cayenne.access.dbsync.CreateIfNoSchemaStrategy" from the dropdown, so that Cayenne creates a new schema on Derby based on the ORM mapping when the application starts.
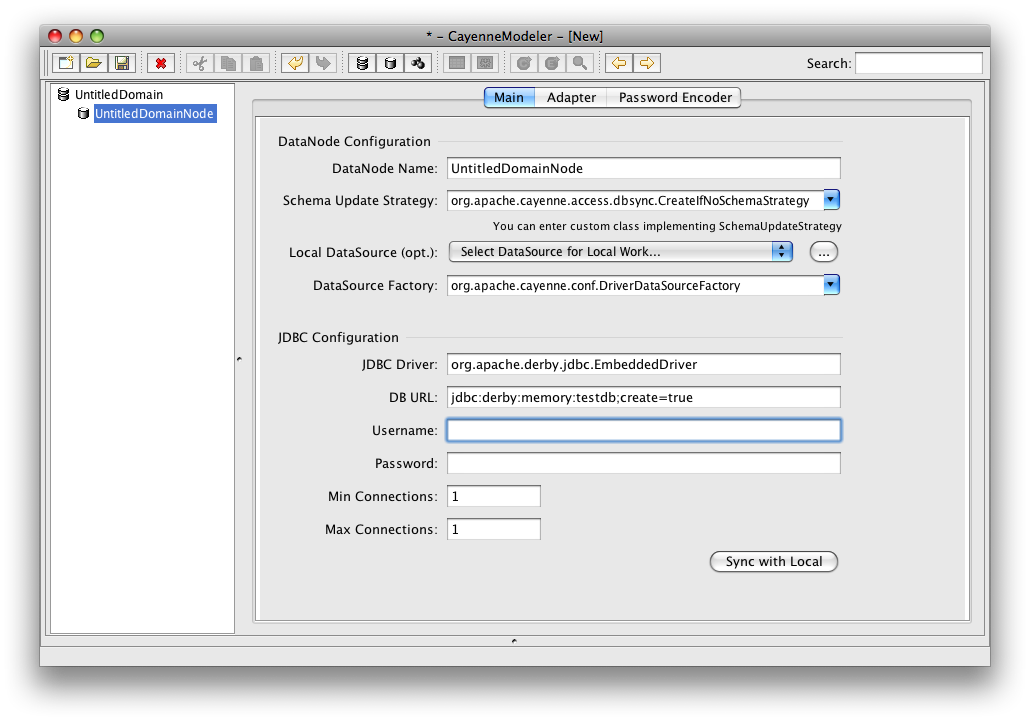
Now you will create a DataMap. DataMap is an object that holds all the mapping information. To create it, click on "Create DataMap" button (or select a corresponding menu item). Note that the newly created DataMap is automatically linked to the DataNode that you created in the previous step. If there is more than one DataNode, you may need to link a DataMap to the correct node manually. In other words a DataMap within DataDomain must point to a database described by the map.
You can leave all the DataMap defaults unchanged except for one - "Java Package". Enter "org.example.cayenne.persistent". This name will later be used for all persistent classes.
Before you proceed with the actual mapping, let's save the project. Click on "Save" button in the toolbar and navigate to the "tutorial" Eclipse project folder that was created earlier in this section and its "src/main/resources" subfolder and save the project there. Now go back to Eclipse, right click on "tutorial" project and select "Refresh", you will see three Cayenne XML files.
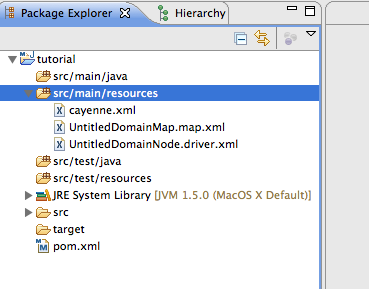
Note that the location of the XML files is not coincidental. Cayenne runtime looks for "cayenne.xml" file in the application CLASSPATH and "src/main/resources" folder should already be a "class folder" in Eclipse for our project (and is also a standard location that Maven would copy to a jar file, if we were using Maven from command-line).
Next Step: Tutorial Object Relational Mapping